Inflammatory Biomarker Reduction With Fostemsavir Over 96 Weeks in Heavily Treatment-Experienced Adults With Multidrug-Resistant HIV-1 in the BRIGHTE Study
- PMID: 39233711
- PMCID: PMC11372475
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofae469
Inflammatory Biomarker Reduction With Fostemsavir Over 96 Weeks in Heavily Treatment-Experienced Adults With Multidrug-Resistant HIV-1 in the BRIGHTE Study
Abstract
Background: Fostemsavir, a first-in-class attachment inhibitor that binds to the viral envelope protein gp120, is approved for heavily treatment-experienced persons with HIV-1 with limited treatment options. We explored changes in immunologic and coagulopathy parameters in the BRIGHTE study: a phase 3 trial that evaluated fostemsavir plus optimized background therapy in heavily treatment-experienced adults with multidrug-resistant HIV-1.
Methods: CD4+ T-cell count, CD4+/CD8+ ratio, soluble CD14, soluble CD163, and D-dimer levels were measured through 96 weeks in participants with 1 or 2 fully active antiretroviral agents available at screening. No formal statistical analyses were performed.
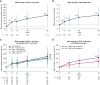
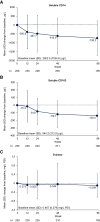
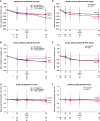
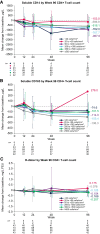
Results: Among 272 participants, increases were observed from baseline to week 96 in CD4+ T-cell count (mean increase, +205 cells/mm3) and CD4+/CD8+ ratio (mean increase, +0.24). The proportion of observed participants with a CD4+/CD8+ ratio ≥0.45 increased from 9% (25/272) at baseline to 40% (85/213) at week 96. From baseline to week 96, we also observed trends toward decreases in the following (mean [SD] change): soluble CD14, -738.2 (981.8) µg/L; soluble CD163, -138.0 (193.4) µg/L; and D-dimer, -0.099 (0.521) mg/L fibrinogen-equivalent units. Decreases in biomarkers were generally observed among subgroups by baseline disease characteristics, virologic response, and CD4+ T-cell count.
Conclusions: These data suggest that heavily treatment-experienced persons with multidrug-resistant HIV-1 treated with fostemsavir + optimized background therapy may have improvements in immune parameters, including markers of monocyte activation and coagulopathy.
Clinical trials registration: NCT02362503 (ClinicalTrials.gov; https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02362503).
Keywords: CD4+ T-cell count; CD4+/CD8+ ratio; biomarkers; fostemsavir; heavily treatment experienced.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. A. C., M. P., S. C., A. P., J. R. C.-M., M. W., F. D., and A. R. T. are or were employees of ViiV Healthcare or GSK at the time of the analysis and may own stock in GSK.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and efficacy of the HIV-1 attachment inhibitor prodrug fostemsavir in heavily treatment-experienced individuals: week 96 results of the phase 3 BRIGHTE study.Lancet HIV. 2020 Nov;7(11):e740-e751. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(20)30240-X. Lancet HIV. 2020. PMID: 33128903 Clinical Trial.
-
Week 240 Efficacy and Safety of Fostemsavir Plus Optimized Background Therapy in Heavily Treatment-Experienced Adults with HIV-1.Infect Dis Ther. 2023 Sep;12(9):2321-2335. doi: 10.1007/s40121-023-00870-6. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Infect Dis Ther. 2023. PMID: 37751019 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term safety and impact of immune recovery in heavily treatment-experienced adults receiving fostemsavir for up to 5 years in the phase 3 BRIGHTE study.Front Immunol. 2024 May 28;15:1394644. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1394644. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38863717 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Fostemsavir in Heavily Treatment-Experienced People With HIV-1.Clin Ther. 2022 Jun;44(6):886-900. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2022.04.007. Epub 2022 May 21. Clin Ther. 2022. PMID: 35610081
-
Fostemsavir resistance in clinical context: a narrative review.Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2025 Mar 24;12:20499361251325103. doi: 10.1177/20499361251325103. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40145022 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

