The geometry of the vergence-accommodation conflict in mixed reality systems
- PMID: 39233779
- PMCID: PMC11371868
- DOI: 10.1007/s10055-024-00991-4
The geometry of the vergence-accommodation conflict in mixed reality systems
Abstract
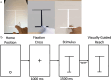
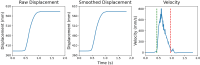
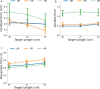
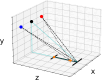
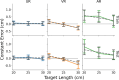
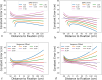
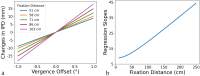
Mixed reality technologies, such as virtual (VR) and augmented (AR) reality, present promising opportunities to advance education and professional training due to their adaptability to diverse contexts. Distortions in the perceived distance in such mediated conditions, however, are well documented and have imposed nontrivial challenges that complicate and limit transferring task performance in a virtual setting to the unmediated reality (UR). One potential source of the distance distortion is the vergence-accommodation conflict-the discrepancy between the depth specified by the eyes' accommodative state and the angle at which the eyes converge to fixate on a target. The present study involved the use of a manual pointing task in UR, VR, and AR to quantify the magnitude of the potential depth distortion in each modality. Conceptualizing the effect of vergence-accommodation offset as a constant offset to the vergence angle, a model was developed based on the stereoscopic viewing geometry. Different versions of the model were used to fit and predict the behavioral data for all modalities. Results confirmed the validity of the conceptualization of vergence-accommodation as a device-specific vergence offset, which predicted up to 66% of the variance in the data. The fitted parameters indicate that, due to the vergence-accommodation conflict, participants' vergence angle was driven outwards by approximately 0.2°, which disrupted the stereoscopic viewing geometry and produced distance distortion in VR and AR. The implications of this finding are discussed in the context of developing virtual environments that minimize the effect of depth distortion.
Keywords: Augmented reality; Depth perception; Manual pointing; Vergence-accommodation conflict; Virtual reality.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Barkokebas R, Ritter C, Sirbu V, Li X, Al-Hussein M (2019) Application of virtual reality in task training in the construction manufacturing industry. In: ISARC. Proceedings of the international symposium on automation and robotics in construction, 36, 796–803
-
- Barrera Machuca MD, Stuerzlinger W (2019) The effect of stereo display deficiencies on virtual hand pointing. In: Proceedings of the 2019 CHI conference on human factors in computing systems, pp 1–14
-
- Batmaz AU, Machuca MDB, Pham DM, Stuerzlinger W (2019) Do head-mounted display stereo deficiencies affect 3D pointing tasks in AR and VR? In: 2019 IEEE conference on virtual reality and 3D user interfaces (VR), pp 585–592
-
- Batmaz AU, Barrera Machuca MD, Sun J, Stuerzlinger W (2022) The effect of the vergence-accommodation conflict on virtual hand pointing in immersive displays. In: CHI conference on human factors in computing systems, pp 1–15
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
