Advances and recent trends in plant-based materials and edible films: a mini-review
- PMID: 39233921
- PMCID: PMC11371721
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1441650
Advances and recent trends in plant-based materials and edible films: a mini-review
Abstract
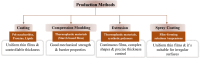
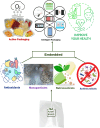
Plant-based materials and edible films have emerged as promising alternatives to conventional packaging materials, offering sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions. This mini-review highlights the significance of plant-based materials derived from polysaccharides, proteins, and lipids, showcasing their renewable and biodegradable nature. The properties of edible films, including mechanical strength, barrier properties, optical characteristics, thermal stability, and shelf-life extension, are explored, showcasing their suitability for food packaging and other applications. Moreover, the application of 3D printing technology allows for customized designs and complex geometries, paving the way for personalized nutrition. Functionalization strategies, such as active and intelligent packaging, incorporation of bioactive compounds, and antimicrobial properties, are also discussed, offering additional functionalities and benefits. Challenges and future directions are identified, emphasizing the importance of sustainability, scalability, regulation, and performance optimization. The potential impact of plant-based materials and edible films is highlighted, ranging from reducing reliance on fossil fuels to mitigating plastic waste and promoting a circular economy. In conclusion, plant-based materials and edible films hold great potential in revolutionizing the packaging industry, offering sustainable alternatives to conventional materials. Embracing these innovations will contribute to reducing plastic waste, promoting a circular economy, and creating a sustainable and resilient planet.
Keywords: edible films; food packaging; nanocomposite; plant-based materials; plastic waste.
Copyright © 2024 Olawade, Wada and Ige.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comprehensive review on starch-based sustainable edible films loaded with bioactive components for food packaging.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Aug;274(Pt 1):133332. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133332. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38914408 Review.
-
A critical review on protein-based smart packaging systems: Understanding the development, characteristics, innovations, and potential applications.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(24):8633-8648. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2202256. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 37114905 Review.
-
Sustainable edible packaging systems based on active compounds from food processing byproducts: A review.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2022 Jan;21(1):198-226. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12870. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2022. PMID: 34907649 Review.
-
Recent advances in plant protein-based sustainable edible film and coatings for applications in the food-pharma industry - Opportunities and challenges: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Mar;296:139698. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.139698. Epub 2025 Jan 9. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 39798769 Review.
-
Plant protein-based nanocomposite films: A review on the used nanomaterials, characteristics, and food packaging applications.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(29):9667-9693. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2070721. Epub 2022 May 6. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 35522084 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Alginate-Chitosan Bioactive Films Containing Essential Oils for Use in Food Packaging.Foods. 2025 Jan 15;14(2):256. doi: 10.3390/foods14020256. Foods. 2025. PMID: 39856921 Free PMC article.
-
Controlled Release of D-Limonene from Biodegradable Films with Enzymatic Treatment.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Aug 17;17(16):2238. doi: 10.3390/polym17162238. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40871185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguirre-Loredo R. Y., Rodríguez-Hernández A. I., Chavarría-Hernández N. (2014). Physical properties of emulsified films based on chitosan and oleic acid. CyTA - J. Food 12, 305–312. 10.1080/19476337.2013.853207 - DOI
-
- Amaraweera S. M., Gunathilake C., Gunawardene O. H. P., Fernando N. M. L., Wanninayaka D. B., Dassanayake R. S., et al. (2021). Development of starch-based materials using current modification techniques and their applications: a review. Molecules 26 (22), 6880. 10.3390/molecules26226880 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources