Crystal Structure of Bifidobacterium bifidum Glycoside Hydrolase Family 110 α-Galactosidase Specific for Blood Group B Antigen
- PMID: 39234034
- PMCID: PMC11368712
- DOI: 10.5458/jag.jag.JAG-2024_0005
Crystal Structure of Bifidobacterium bifidum Glycoside Hydrolase Family 110 α-Galactosidase Specific for Blood Group B Antigen
Abstract
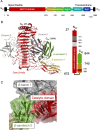
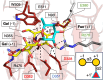
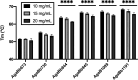
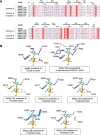
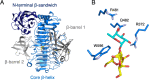
To overcome incompatibility issues and increase the possibility of blood transfusion, technologies that enable efficient conversion of A- and B-type red blood cells to the universal donor O-type is desirable. Although several blood type-converting enzymes have been identified, detailed understanding about their molecular functions is limited. α-Galactosidase from Bifidobacterium bifidum JCM 1254 (AgaBb), belonging to glycoside hydrolase (GH) 110 subfamily A, specifically acts on blood group B antigen. Here we present the crystal structure of AgaBb, including the catalytic GH110 domain and part of the C-terminal uncharacterized regions. Based on this structure, we deduced a possible binding mechanism of blood group B antigen to the active site. Site-directed mutagenesis confirmed that R270 and E380 recognize the fucose moiety in the B antigen. Thermal shift assay revealed that the C-terminal uncharacterized region significantly contributes to protein stability. This region is shared only among GH110 enzymes from B. bifidum and some Ruminococcus species. The elucidation of the molecular basis for the specific recognition of blood group B antigen is expected to lead to the practical application of blood group conversion enzymes in the future.
Keywords: Bifidobacterium; Blood group conversion; crystal structure; glycoside hydrolase; mucin; α-galactosidase.
2024 by The Japanese Society of Applied Glycoscience.
Conflict of interest statement
Takura Wakinaka is an employee of Yamasa Corporation.
Figures
References
-
- Rydberg L. ABO-incompatibility in solid organ transplantation. Transfus Med. 2001; 11: 325-42. - PubMed
-
- Galili U. Xenotransplantation and ABO incompatible transplantation: The similarities they share. Transfus Apher Sci. 2006; 35: 45-58. - PubMed
-
- Rossez Y, Maes E, Lefebvre Darroman T, Gosset P, Ecobichon C, Joncquel Chevalier Curt M, et al. Almost all human gastric mucin O-glycans harbor blood group A, B or H antigens and are potential binding sites for Helicobacter pylori. Glycobiology. 2012; 22: 1193-206. - PubMed
-
- Misevic G, Misevic G. ABO blood group system. Blood Genom. 2018; 2: 71-84.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
