Health inequalities in a middle-income country: a systematic review of the Costa Rican case
- PMID: 39234081
- PMCID: PMC11373478
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1397576
Health inequalities in a middle-income country: a systematic review of the Costa Rican case
Abstract
Objective: This study systematically reviews evidence of socioeconomic health disparities in Costa Rica, a middle-income country, to elucidate the relationship between socioeconomic status and health outcomes.
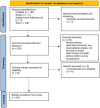
Methods: Published studies were identified through a systematic review of PubMed (English) and Scielo (Spanish) databases from December 2023 to January 2024, following PRISMA guidelines. Search terms included socioeconomic status, social determinants, social gradient in health, and health inequalities.
Results: Of 236 identified references, 55 met the inclusion criteria. Findings were categorized into health inequalities in mortality (among the general population, infants, and older adults), life expectancy, cause-specific mortality, and health determinants or risk factors mediating the association between the social environment and health. The studies indicate higher mortality among the most disadvantaged groups, including deaths from respiratory diseases, violence, and infections. Higher socioeconomic status was associated with lower mortality rates in the 1990s, indicating a positive social gradient in health (RII = 1.3, CI [1.1-1.5]). Disparities were less pronounced among older adults. Urban areas exhibited concentrated wealth and increased risky behaviors, while rural areas, despite greater socioeconomic deprivation, showed a lower prevalence of risky behaviors. Regarding smoking, people living in rural areas smoked significantly less than those in urban areas (7% vs. 10%). Despite the relatively equitable distribution of public primary healthcare, disparities persisted in the timely diagnosis and treatment of chronic diseases. Cancer survival rates post-diagnosis were positively correlated with the wealth of districts (1.23 [1.12-1.35] for all cancers combined).
Conclusion: The study highlights the existence of social health inequalities in Costa Rica. However, despite being one of the most unequal OECD countries, Costa Rica shows relatively modest social gradients in health compared to other middle and high-income nations. This phenomenon can be attributed to distinctive social patterns in health behaviors and the equalizing influence of the universal healthcare system.
Keywords: Costa Rica; health inequalities; health inequities; low and middle-income country; social determinants of health; systematic review.
Copyright © 2024 Barboza-Solis, Herrero and Fantin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Social Determinants of Health. Available at: https://www.who.int/health-topics/social-determinants-of-health#tab=tab_1 (Accessed January 2024).
-
- Whitehead M, Dahlgren G. Concepts and principles for tackling social inequities in health: Levelling up part 1. Copenhagen: World Health Organization. (2006). 34 p.
-
- Stringhini S, Carmeli C, Jokela M, Avendano M, Muennig P, Guida F, et al. Socioeconomic status and the 25 x 25 risk factors as determinants of premature mortality: a multicohort study and meta-analysis of 1.7 million men and women. Lancet. (2017) 389:1229–37. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32380-7, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous