Increasing situational awareness through nowcasting of the reproduction number
- PMID: 39234082
- PMCID: PMC11371679
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1430920
Increasing situational awareness through nowcasting of the reproduction number
Abstract
Background: The time-varying reproduction number R is a critical variable for situational awareness during infectious disease outbreaks; however, delays between infection and reporting of cases hinder its accurate estimation in real-time. A number of nowcasting methods, leveraging available information on data consolidation delays, have been proposed to mitigate this problem.
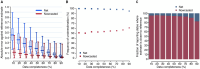
Methods: In this work, we retrospectively validate the use of a nowcasting algorithm during 18 months of the COVID-19 pandemic in Italy by quantitatively assessing its performance against standard methods for the estimation of R.
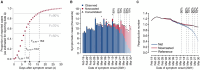
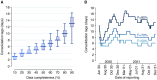
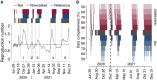
Results: Nowcasting significantly reduced the median lag in the estimation of R from 13 to 8 days, while concurrently enhancing accuracy. Furthermore, it allowed the detection of periods of epidemic growth with a lead of between 6 and 23 days.
Conclusions: Nowcasting augments epidemic awareness, empowering better informed public health responses.
Keywords: epidemic surveillance; nowcasting; outbreaks; reproduction number; situational awareness.
Copyright © 2024 Bizzotto, Guzzetta, Marziano, Del Manso, Mateo Urdiales, Petrone, Cannone, Sacco, Poletti, Manica, Zardini, Trentini, Fabiani, Bella, Riccardo, Pezzotti, Ajelli and Merler.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- O'Driscoll M, Harry C, Donnelly CA, Cori A, Dorigatti I. A comparative analysis of statistical methods to estimate the reproduction number in emerging epidemics, with implications for the current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Clin Infect Dis. (2021) 73:e215–23. 10.1093/cid/ciaa1599 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

