Optimization path of primary public health service talent team construction: a largescale survey in Huaihai Economic Zone, China
- PMID: 39234097
- PMCID: PMC11371681
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1399857
Optimization path of primary public health service talent team construction: a largescale survey in Huaihai Economic Zone, China
Abstract
Background: The primary public health service system is indispensable for the implementation of the "Healthy China 2030" strategy, and primary healthcare workers, as the key drivers of this system, play a pivotal role in its development and establishment to ensure population well-being. In developing countries, such as China, primary public health systems are still weak, and in order to address this phenomenon, health system reform is needed, and primary public health personnel are crucial to health system reform. The current situation of primary public health workers in low-income and developing countries is characterized by varying degrees of problems that need improvement.
Objectives: The purpose of this study is to understand the current situation of primary public health service workforce building, analyze the existing problems of the workforce, put forward suggestions for improvement and explore countermeasures, and provide Chinese wisdom and a reference basis for primary public health workforce building in the world, especially in developing countries.
Methods: Combining the Work-Family Conflict Scale, Copenhagen Burnout Inventory, Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire, and Turnover Intention Scale, a relevant survey questionnaire was designed to quantitatively investigate the baseline characteristics of primary public health service institutions and their staff in four representative cities in the Huaihai Economic Zone: Xuzhou in Jiangsu Province, Linyi in Shandong Province, Shangqiu in Henan Province, and Huaibei in Anhui Province. The collected data were analyzed and processed using SPSS 25.0 statistical analysis software through univariate analysis and logistic regression analyses. Methods such as one-way ANOVA, Logistic regression analysis, and independent samples t-test were used to analyze the influencing factors of primary public health workforce development.
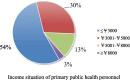
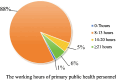
Results: The current work intensity at the primary public health level is currently high, the salary and benefits cannot meet the needs of most primary public health personnel, and the competition between work and family in terms of time and resources is pronounced, and the majority of primary public health personnel are dissatisfied with the status quo of "doing more work for less reward" and the poor social security. Emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and a sense of personal accomplishment were positively correlated with the tendency to leave (all p < 0.01), and the burnout and emotional exhaustion of primary public health workers were intense.
Conclusion: Primary public health personnel play an important role in providing primary public health services. However, the current working conditions of junior public health personnel in the Huaihai Economic Zone are influenced by factors such as workload, income level, and employment situation improvement, leading to low job satisfaction, significant work-family conflicts, and high turnover intention. In this context, based on the opinions of grassroots administrative departments and internationally relevant experiences, a series of suggestions have been proposed to improve the professional service level, job satisfaction, and occupational identity of staff members. These suggestions make valuable contributions to both the Huaihai Economic Zone and countries worldwide in safeguarding individual health and promoting national primary healthcare reform.
Keywords: Huaihai Economic Zone; burnout; primary public health service; team construction; work–family conflict.
Copyright © 2024 Ni, Wang, Wen, Fang, Xu, Wu, Sawmadal and Jama.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- The Sixty-Ninth World Health Assembly . Global strategy for health human resources: health manpower 2030. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2016).
-
- Chaoxin W, Shi Jianwei X, Gang CY, Hui W. Thinking and prospect of the "pain point" of public health outstanding talent training in China. Proc Chin Acad Sci. (2020) 35:297–305. doi: 10.16418/j.issn.1000-3045.20200221002 - DOI
-
- Zhiping L. Current state and reform trends in primary health care in the United States. Chin J General Pract. (2015) 9:732–4. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-7368.2015.09.026 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources