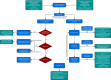
Placental abruption
- PMID: 39234154
- PMCID: PMC11368588
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjae.2024.05.001
Placental abruption
Keywords: obstetrics; placental abruption, uterine haemorrhage; placental diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
AL is an editor and editorial board member of BJA Education. CDS declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sher G. A rational basis for the management of abruptio placentae. J Reprod Med. 1978;21:123–129. - PubMed
-
- Oyelese Y., Ananth C.V. Placental abruption. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;108:1005–1016. - PubMed
-
- Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists Green-top guideline No. 63. Antepartum haemorrhage. https://www.rcog.org.uk/guidance/browse-all-guidance/green-top-guideline... Available from:
-
- Ananth CV, Kinzler WL. Acute placental abruption: pathophysiology, clinical features, diagnosis, and consequences. In: UpToDate, Wolters Kleuwer. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com (accessed 25 October 2023).
-
- Tikkanen M. Placental abruption: epidemiology, risk factors and consequences. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2010;90:140–149. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources