Bioassay-Guided Fractionation of Acetone and Methanol Extracts of Quercus infectoria Galls with Antimalarial Properties
- PMID: 39234468
- PMCID: PMC11371400
- DOI: 10.21315/tlsr2024.35.2.8
Bioassay-Guided Fractionation of Acetone and Methanol Extracts of Quercus infectoria Galls with Antimalarial Properties
Abstract
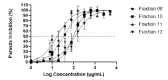
The antimalarial properties of crude extracts from Quercus infectoria galls were investigated through bioassay-guided fractionation. Acetone (QIA) and methanol (QIM) crude extracts have been reported to have promising antimalarial activity against Plasmodium falciparum (3D7 strain). These extracts were subjected to fractionation using automated preparative high-performance liquid chromatography (prep-HPLC) to identify the most active fractions. Nine fractions were isolated from each extract, of which the fractions QIA11 and QIM16 showed antimalarial activity, with IC50 values of 17.65 ± 1.82 μg/mL and 24.21 ± 1.88 μg/mL, respectively. In comparison, the standard antimalarial drug artemisinin has an IC50 value of 0.004 ± 0.001 μg/mL). Through high-resolution liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (HR-LCMS) analysis of the fractions, four known compounds were successfully identified: gallic acid, ellagic acid, 1,3,6-tris-o-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)-beta-d-glucose and 1-O,6-O-digalloyl-beta-D-glucose.
Sifat-sifat antimalaria ekstrak-ekstrak mentah dari biji Quercus infectoria dikaji melalui fraksinasi berpandukan bioasai. Ekstrak mentah aseton (QIA) dan metanol (QIM) dilaporkan sebelum ini mempunyai aktiviti antimalaria terhadap Plasmodium falciparum (strain 3D7). Ekstrak-ekstrak ini melalui fraksinasi menggunakan persediaan automatik kromatografi cecair berprestasi tinggi (prep-HPLC) untuk mengenal pasti fraksi yang paling aktif. Sembilan fraksi telah diasingkan daripada setiap ekstrak, di mana fraksi QIA11 dan QIM16 menunjukkan aktiviti antimalaria dengan nilai IC50 17.65 ± 1.82 μg / mL dan 24.21 ± 1.88 μg/mL, masing-masing dibandingkan dengan ubat antimalaria standard, artemisinin (IC50 = 0.004 ± 0.001 μg/mL). Analisa menggunakan kromatografi cecair beresolusi tinggi bersama dengan spektrometri jisim (HR-LCMS) berjaya mengenal pasti empat sebatian: asid gallic, asid ellagic, 1,3,6-tris-o-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)-beta-dglukosa dan 1-O, 6-O-digalloyl-beta-D-glukosa.
Keywords: Antimalarial Activity; HR-LCMS; Plasmodium falciparum; Preparative-HPLC; Quercus infectoria.
© Penerbit Universiti Sains Malaysia, 2024.
Figures




References
-
- Abdullah AR, Hapidin H, Abdullah H. Phytochemical analysis of Quercus infectoria galls extracts using FTIR, LC-MS and MS/MS analysis. Research Journal of Biotechnology. 2017;12(12):55–61.
-
- Abdul Haque AS, Wasim A, Khan MR, Hasan A. Ethnopharmacology of Quercus infectoria galls: A review. Hippocratic Journal of Unani Medicine. 2016;11(3):105–118.
-
- Arya A, Foko LPK, Chaudhry S, Sharma A, Singh V. Artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) and drug resistance molecular markers: A systematic review of clinical studies from two malaria endemic regions – India and Sub-Saharan Africa. International Journal for Parasitology: Drugs and Drug Resistance. 2021;15:43–56. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2020.11.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
