Potential mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of liver cirrhosis: a focus on gut microbiota
- PMID: 39234554
- PMCID: PMC11371771
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1407991
Potential mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of liver cirrhosis: a focus on gut microbiota
Abstract
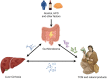
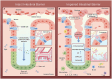
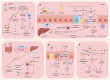
Cirrhosis, a pathological stage that develops from various chronic liver diseases, is characterized by liver fibrosis, pseudolobular formation, and chronic inflammation. When it progresses to the decompensated phase, the mortality rate of cirrhosis can reach 80%. The role of gut microbiota in the progression of liver diseases has received significant attention. Numerous studies have shown that regulating gut microbiota has significant therapeutic effects on preventing and reversing liver cirrhosis. This article reviewed the mechanisms by which gut microbiota influence liver cirrhosis, explaining the effective therapeutic effects of traditional Chinese medicine. Through multi-directional regulation involving signaling pathways, gut microbiota diversity, and restoration of intestinal barrier function, traditional Chinese medicine has been promising in ameliorating liver cirrhosis, providing treatment options and pharmacological guidance for the occurrence and development of liver cirrhosis.
Keywords: gut microbiota; liver cirrhosis; microbial metabolites; natural products; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2024 Sun, Zhang, Lv and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Assimakopoulos S. F., Tsamandas A. C., Tsiaoussis G. I., Karatza E., Triantos C., Vagianos C. E., et al. (2012). Altered intestinal tight junctions’ expression in patients with liver cirrhosis: a pathogenetic mechanism of intestinal hyperpermeability. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 42, 439–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2011.02609.x, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

