Glymphatic System and Psychiatric Disorders: A Rapid Comprehensive Scoping Review
- PMID: 39234773
- PMCID: PMC11333792
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X22666240130091235
Glymphatic System and Psychiatric Disorders: A Rapid Comprehensive Scoping Review
Abstract
Background: Since discovering the glymphatic system, there has been a looming interest in exploring its relationship with psychiatric disorders. Recently, increasing evidence suggests an involvement of the glymphatic system in the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders. However, clear data are still lacking. In this context, this rapid comprehensive PRISMA-ScR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews) scoping review aims to identify and analyze current evidence about the relation between the glymphatic system and psychiatric disorders.
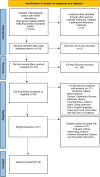
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive review of the literature and then proceeded to discuss the findings narratively. Tables were then constructed and articles were sorted according to authors, year, title, location of study, sample size, psychiatric disorder, the aim of the study, principal findings, implications.
Results: Twenty papers were identified as eligible, among which 2 articles on Schizophrenia, 1 on Autism Spectrum Disorders, 2 on Depression, 1 on Depression and Trauma-related Disorders, 1 on Depression and Anxiety, 2 on Anxiety and Sleep Disorders, 8 on Sleep Disorders, 2 on Alcohol use disorder and 1 on Cocaine Use Disorder.
Conclusion: This review suggests a correlation between the glymphatic system and several psychiatric disorders: Schizophrenia, Depression, Anxiety Disorders, Sleep Disorders, Alcohol Use Disorder, Cocaine Use Disorder, Trauma-Related Disorders, and Autism Spectrum Disorders. Impairment of the glymphatic system could play a role in Trauma-Related Disorders, Alcohol Use Disorders, Cocaine Use Disorders, Sleep Disorders, Depression, and Autism Spectrum Disorders. It is important to implement research on this topic and adopt standardized markers and radio diagnostic tools.
Keywords: Glymphatic system; aquaporin-4; astrocytes; depression.; mood disorders; psychiatric disorders.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures
References
-
- Iliff J.J., Wang M., Liao Y., Plogg B.A., Peng W., Gundersen G.A., Benveniste H., Vates G.E., Deane R., Goldman S.A., Nagelhus E.A., Nedergaard M. A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid β. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012;4(147):147ra111. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003748. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Troili F., Cipollini V., Moci M., Morena E., Palotai M., Rinaldi V., Romano C., Ristori G., Giubilei F., Salvetti M., Orzi F., Guttmann C.R.G., Cavallari M. Perivascular Unit: This must be the place. the anatomical crossroad between the immune, vascular and nervous system. Front. Neuroanat. 2020;14:17. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2020.00017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical