Lessons learned from the FinnDiane Study: Epidemiology and metabolic risk factors for diabetic kidney disease in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 39235140
- PMCID: PMC11733665
- DOI: 10.1111/dme.15431
Lessons learned from the FinnDiane Study: Epidemiology and metabolic risk factors for diabetic kidney disease in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Aims: Across its operational span of more than 25 years, the observational, nationwide, multicentre Finnish Diabetic Nephropathy (FinnDiane) Study has aimed to unravel mechanisms underlying diabetic kidney disease, with a special focus on its metabolic risk factors. We sought to compile key findings relating to this topic and to offer a current perspective on the natural course of diabetic kidney disease among individuals with type 1 diabetes.
Methods: In this narrative review, articles relevant to the subject published by the FinnDiane Study were identified and summarized together with work published by others, when relevant.
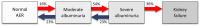
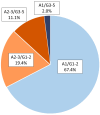
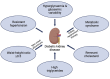
Results: The FinnDiane Study has underscored the significance of dysglycaemia and insulin resistance, increased visceral fat mass, hypertension and dyslipidaemia-particularly high triglycerides and remnant cholesterol-as risk factors for diabetic kidney disease. Factors like abdominal obesity seem to influence the early stages of the disease, while the presence of the metabolic syndrome becomes implicated at later stages. Epidemiological reports have revealed that after an initial decline, the cumulative incidence of albuminuria plateaued post-1980s, with the progression rate to kidney failure remaining high. Fortunately, 23% of the FinnDiane cohort regressed to less advanced stages of albuminuria, improving their overall prognosis.
Conclusion: A substantial burden of albuminuria associated with type 1 diabetes persists, and therefore, novel kidney-protecting therapies are highly awaited. In addition, given that metabolic factors influence the progression of diabetic kidney disease both in its early and advanced stages, emphasis should be placed on ensuring that their treatment targets are met.
Keywords: albuminuria; diabetic kidney disease; dyslipidaemia; hypertension; insulin resistance; metabolic syndrome; type 1 diabetes.
© 2024 The Author(s). Diabetic Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Diabetes UK.
Conflict of interest statement
F.J.S. reports receiving lecture fees from AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim. P‐H.G. reports receiving lecture fees from Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Elo Water, Genzyme, Medscape, Merck, Sharp & Dohme, Mundipharma, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, PeerVoice, Sanofi and Sciarc. P‐H.G. reports being an advisory board member for AbbVie, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Medscape, Merck, Sharp& Dohme, Mundipharma, Nestlé, Novartis, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures
References
-
- Jansson Sigfrids F, Groop PH, Harjutsalo V. Incidence rate patterns, cumulative incidence, and time trends for moderate and severe albuminuria in individuals diagnosed with type 1 diabetes aged 0‐14 years: a population‐based retrospective cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10(7):489‐498. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00099-7 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

