Content validity of the Leicester Cough Questionnaire in adults with refractory or unexplained chronic cough: a qualitative interview study
- PMID: 39235438
- PMCID: PMC11378222
- DOI: 10.1177/17534666241274261
Content validity of the Leicester Cough Questionnaire in adults with refractory or unexplained chronic cough: a qualitative interview study
Abstract
Background: Chronic cough, a cough lasting >8 weeks, includes refractory chronic cough (RCC) and unexplained chronic cough (UCC). Patient-reported outcome (PRO) measures are needed to better understand chronic cough impacts that matter most to patients. The 19-item Leicester Cough Questionnaire (LCQ), an existing PRO measure of chronic cough, assesses impacts of cough across physical, psychological, and social domains. However, the content validity of the LCQ evaluating these concepts in patients with RCC/UCC had not been established.
Objectives: To evaluate the content validity of the LCQ in patients with RCC/UCC.
Design: A cross-sectional, qualitative interview study.
Methods: First, previously completed qualitative interview results in adults with RCC/UCC (N = 30) were evaluated and mapped to LCQ concepts. Next, a clinical cough expert reviewed each LCQ item and assessed the salience of its concepts for patients with RCC/UCC. Finally, semistructured interviews-including both concept elicitation and cognitive debriefing-were conducted in adults with RCC/UCC (N = 20) to elicit a comprehensive set of participant experiences and to assess the appropriateness of using the LCQ in this population.
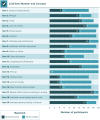
Results: Concepts reported in the past and present qualitative interviews were included across all LCQ items, and most impacts reported to be the "most bothersome" were assessed in the LCQ. In the current study, all participants indicated that reduced cough frequency would be an important treatment target. During cognitive debriefing, each LCQ item was endorsed by ⩾70% of participants. Additionally, participants were generally able to understand, recall, and select a response for each LCQ item. All participants and the clinical expert indicated that the LCQ was appropriate and assessed the impacts most relevant to patients with RCC/UCC.
Conclusion: Our findings support the content validity of the LCQ and demonstrate that this measure is fit-for-purpose and includes important cough impacts in adults with RCC/UCC.
Keywords: Leicester Cough Questionnaire; chronic cough; content validity; cough-specific health-related quality of life; patient-reported outcome; qualitative interviews; refractory chronic cough; unexplained chronic cough.
Conflict of interest statement
A.M. Nguyen, C. La Rosa, and A.G. Cornell are employees of Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and hold shares and/or stock options in Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. M.R. Sher is a Clinical investigator, Consultant and Speaker for Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. J.A. Bernstein is a principal investigator and consultant for both GSK and Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. S.S. Birring has received consultancy fees, research grants, and LCQ developer fees from Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. C.D. Romano, M. Mayorga, M. Milien, and C. Ervin are full-time employees of RTI Health Solutions, an independent nonprofit research organization, which was retained by Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, to conduct the research which is the subject of this manuscript.
Figures






References
-
- Song WJ, Chang YS, Faruqi S, et al. The global epidemiology of chronic cough in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir J 2015; 45(5): 1479–1481. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

