SETD1B mutations confer apoptosis resistance and BCL2 independence in B cell lymphoma
- PMID: 39235528
- PMCID: PMC11380151
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20231143
SETD1B mutations confer apoptosis resistance and BCL2 independence in B cell lymphoma
Abstract
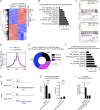
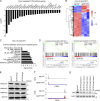
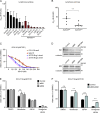
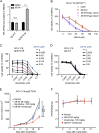
The translocation t(14;18) activates BCL2 and is considered the initiating genetic lesion in most follicular lymphomas (FL). Surprisingly, FL patients fail to respond to the BCL2 inhibitor, Venetoclax. We show that mutations and deletions affecting the histone lysine methyltransferase SETD1B (KMT2G) occur in 7% of FLs and 16% of diffuse large B cell lymphomas (DLBCL). Deficiency in SETD1B confers striking resistance to Venetoclax and an experimental MCL-1 inhibitor. SETD1B also acts as a tumor suppressor and cooperates with the loss of KMT2D in lymphoma development in vivo. Consistently, loss of SETD1B in human lymphomas typically coincides with loss of KMT2D. Mechanistically, SETD1B is required for the expression of several proapoptotic BCL2 family proteins. Conversely, inhibitors of the KDM5 histone H3K4 demethylases restore BIM and BIK expression and synergize with Venetoclax in SETD1B-deficient lymphomas. These results establish SETD1B as an epigenetic regulator of cell death and reveal a pharmacological strategy to augment Venetoclax sensitivity in lymphoma.
© 2024 Portelinha et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: N.K. Aryal works for AstraZeneca and may own stocks of the company. O. Tavana reported personal fees from AstraZeneca outside the submitted work; and being an employee and shareholder of AstraZeneca. A. Dogan reported research support for AstraZeneca, not related to this work. A. Younes reported being currently employed by AstraZeneca. A.M. Melnick reported grants from Janssen, Daiichi Sankyo, Epizyme, AstraZeneca, and Treeline Biosciences during the conduct of the study; and personal fees from Treeline Biosciences and Ipsen outside the submitted work. H-.G. Wendel reported grants from AstraZeneca during the conduct of the study. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures


References
-
- Agarwal, R., Chan Y.C., Tam C.S., Hunter T., Vassiliadis D., Teh C.E., Thijssen R., Yeh P., Wong S.Q., Ftouni S., et al. . 2019. Dynamic molecular monitoring reveals that SWI-SNF mutations mediate resistance to ibrutinib plus venetoclax in mantle cell lymphoma. Nat. Med. 25:119–129. 10.1038/s41591-018-0243-z - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bledau, A.S., Schmidt K., Neumann K., Hill U., Ciotta G., Gupta A., Torres D.C., Fu J., Kranz A., Stewart A.F., and Anastassiadis K.. 2014. The H3K4 methyltransferase Setd1a is first required at the epiblast stage, whereas Setd1b becomes essential after gastrulation. Development. 141:1022–1035. 10.1242/dev.098152 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blombery, P., Anderson M.A., Gong J.N., Thijssen R., Birkinshaw R.W., Thompson E.R., Teh C.E., Nguyen T., Xu Z., Flensburg C., et al. . 2019a. Acquisition of the recurrent Gly101Val mutation in BCL2 confers resistance to venetoclax in patients with progressive chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Discov. 9:342–353. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1119 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Follicular Lymphoma Foundation
- LRF/Lymphoma Research Foundation/United States
- LLS SCOR 7021-20/Leukemia and Lymphoma Society
- R35 CA252982/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Geoffrey Beene Cancer Research Center
- P50 CA217694/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA217694/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- I10-0064/Starr Cancer Consortium
- R35 CA220499/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA229086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA266279/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- SK2021-1271/Astrazeneca
- CE230100001/Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence for the Mathematical Analysis of Cellular Systems
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Chemotherapy Foundation
- Institute for Follicular Lymphoma Innovation
- Sam Waxman Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

