Spatio-temporal EEG dynamics during decision-making in online poker players with problem gambling
- PMID: 39235871
- PMCID: PMC11457024
- DOI: 10.1556/2006.2024.00048
Spatio-temporal EEG dynamics during decision-making in online poker players with problem gambling
Abstract
Background and aims: Gambling activity evolves along a continuum from recreational to Gambling Disorder (GD) and a particular challenge is to identify whether there are some neurophysiological particularities already present in gamblers at an early stage. Our main goal was to determine whether, in the gamblers' population, neural responses generated during uncertain decisions were different depending on problematic gambling risk defined by the Canadian Problem Gambling Index (CPGI). We tested the following hypothesis, that the Problem Gambling group would show a different brain activity related to outcomes processing than people with low risk.
Methods: For this purpose, we established a relatively homogeneous population of Online Poker Players divided into two groups according to the CPGI (Low Risk and Problem Gambling). By means of high-density EEG, we compared the spatio-temporal dynamics generated during the completion of the Iowa Gambling Task.
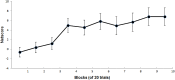
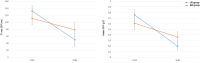
Results: One specific topographic map was observed between 150-175 ms after a negative outcome for both groups, whereas it was displayed in the win condition only for the Problem Gambling group. We found that the Global Field Power of this map was negatively correlated with participants' adherence to a strategy. Source localization identified Anterior Cingulate Cortex and Temporal regions as generators of this map.
Discussion and conclusions: Reward hypersensitivity EEG responses identified in the early outcome process could constitute a potential biomarker of problematic gambling.
Keywords: Iowa Gambling Task; decision-making; high-density EEG; problem gambling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Manuel diagnostique et statistique des troubles mentaux (DSM-5). Elsevier Masson. - PubMed
-
- Barlow, R. L., Alsiö, J., Jupp, B., Rabinovich, R., Shrestha, S., Roberts, A. C., … Dalley, J. W. (2015). Markers of serotonergic function in the orbitofrontal cortex and dorsal Raphé nucleus predict individual variation in spatial-discrimination serial reversal learning. Neuropsychopharmacology, 40(7), 1619–1630. 10.1038/npp.2014.335. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

