Gold nanorod-assisted theranostic solution for nonvisible residual disease in bladder cancer
- PMID: 39236242
- PMCID: PMC11406305
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2411583121
Gold nanorod-assisted theranostic solution for nonvisible residual disease in bladder cancer
Abstract
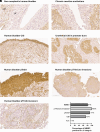
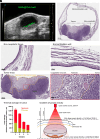
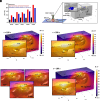
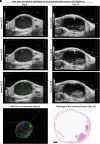
Residual nonvisible bladder cancer after proper treatment caused by technological and therapeutic limitations is responsible for tumor relapse and progression. This study aimed to demonstrate the feasibility of a solution for simultaneous detection and treatment of bladder cancer lesions smaller than one millimeter. The α5β1 integrin was identified as a specific marker in 81% of human high-grade nonmuscle invasive bladder cancers and used as a target for the delivery of targeted gold nanorods (GNRs). In a preclinical model of orthotopic bladder cancer expressing the α5β1 integrin, the photoacoustic imaging of targeted GNRs visualized lesions smaller than one millimeter, and their irradiation with continuous laser was used to induce GNR-assisted hyperthermia. Necrosis of the tumor mass, improved survival, and computational modeling were applied to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of this solution. Our study highlights the potential of the GNR-assisted theranostic strategy as a complementary solution in clinical practice to reduce the risk of nonvisible residual bladder cancer after current treatment. Further validation through clinical studies will support the findings of the present study.
Keywords: bladder tumor; computational modeling; hyperthermia; nanoparticles; photoacoustic imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:F.C., A.C., M.A., I.L., E.A., M. Maturi, E.L., and M.C.F. are inventors of patents regarding GNRs functionalized with peptide Iso4.
Figures

References
-
- Ferlay J., et al. , Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 136, E359–386 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Comperat E., et al. , Clinicopathological characteristics of urothelial bladder cancer in patients less than 40 years old. Virchows Arch. 466, 589–594 (2015). - PubMed
-
- European Association of Urology, Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer, Chapter 5: Diagnosis. https://uroweb.org/guidelines/non-muscle-invasive-bladder-cancer/chapter.... Accessed 1 June 2014.
-
- Rakesh Heer R. L., et al. , A randomized trial of PHOTOdynamic surgery in non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer. NEJM Evid. 1, EVIDoa2200092 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

