Phase I/Ib Trial of Inavolisib Plus Palbociclib and Endocrine Therapy for PIK3CA-Mutated, Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer
- PMID: 39236276
- PMCID: PMC11575912
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.24.00110
Phase I/Ib Trial of Inavolisib Plus Palbociclib and Endocrine Therapy for PIK3CA-Mutated, Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PK), and preliminary antitumor activity of inavolisib, a potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor of p110α that promotes the degradation of mutated p110α, in combination with palbociclib and endocrine therapy (ET), in a phase I/Ib study in patients with PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative locally advanced/metastatic breast cancer (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03006172).
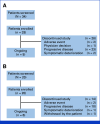
Methods: Women ≥18 years of age received inavolisib, palbociclib, and letrozole (Inavo + Palbo + Letro arm) or fulvestrant (Inavo + Palbo + Fulv arm) until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression. The primary objective was to evaluate safety or tolerability.
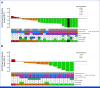
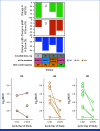
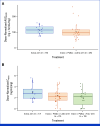
Results: Fifty-three patients were included, 33 in the Inavo + Palbo + Letro arm and 20 in the Inavo + Palbo + Fulv arm. Median duration of inavolisib treatment was 15.7 and 20.8 months (cutoff: March 27, 2023), respectively. Treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) occurred in all patients; the most frequent were stomatitis, hyperglycemia, and diarrhea; grade ≥3 any TRAE rates were 87.9% and 85.0%; 6.1% and 10.0% discontinued any treatment due to TRAEs in the Inavo + Palbo + Letro and Inavo + Palbo + Fulv arms, respectively. No PK drug-drug interactions (DDIs) were observed among the study treatments when administered. Confirmed objective response rates were 52.0% and 40.0% in patients with measurable disease, and median progression-free survival was 23.3 and 35.0 months in the Inavo + Palbo + Letro and Inavo + Palbo + Fulv arms, respectively. Available paired pre- and on-treatment tumor tissue and circulating tumor DNA analyses confirmed the effects of study treatment on pharmacodynamic and pathophysiologic biomarkers of response.
Conclusion: Inavolisib plus palbociclib and ET demonstrated a manageable safety profile, lack of DDIs, and promising preliminary antitumor activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inavolisib plus letrozole or fulvestrant in PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer (GO39374): An open-label, multicentre, dose-escalation and dose-expansion phase 1/1b study.Eur J Cancer. 2025 May 15;221:115397. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2025.115397. Epub 2025 Mar 30. Eur J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40203765 Clinical Trial.
-
Inavolisib-Based Therapy in PIK3CA-Mutated Advanced Breast Cancer.N Engl J Med. 2024 Oct 31;391(17):1584-1596. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2404625. N Engl J Med. 2024. PMID: 39476340 Clinical Trial.
-
Overall Survival with Inavolisib in PIK3CA-Mutated Advanced Breast Cancer.N Engl J Med. 2025 Jul 10;393(2):151-161. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2501796. Epub 2025 May 31. N Engl J Med. 2025. PMID: 40454641 Clinical Trial.
-
Inavolisib: First Approval.Drugs. 2025 Feb;85(2):271-278. doi: 10.1007/s40265-024-02136-y. Epub 2025 Jan 28. Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39873916 Review.
-
Palbociclib: A Novel Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor for Hormone Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer.Ann Pharmacother. 2015 Nov;49(11):1252-60. doi: 10.1177/1060028015602273. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Ann Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 26324355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Biological Roles and Clinical Applications of the PI3K/AKT Pathway in Targeted Therapy Resistance in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 13;25(24):13376. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413376. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The regulatory role of CDK4/6 inhibitors in tumor immunity and the potential value of tumor immunotherapy (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Aug;56(2):123. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5564. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40511560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A high affinity pan-PI3K binding module supports selective targeted protein degradation of PI3Kα.Chem Sci. 2023 Dec 12;15(2):683-691. doi: 10.1039/d3sc04629j. eCollection 2024 Jan 3. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 38179525 Free PMC article.
-
Buenos Aires Breast Cancer Symposium (BA-BCS 2024) A Second Successful "Trial" for Bringing Together both World Hemispheres To Debate the Future of Translational Breast Cancer Research.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2025 Mar 15;30(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s10911-025-09577-5. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2025. PMID: 40088327
-
Treatment strategies targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mechanistic target of rapamycin pathway against triple-negative breast cancer.World J Clin Oncol. 2025 May 24;16(5):104623. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i5.104623. World J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40503407 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DeSantis CE, Ma J, Gaudet MM, et al. Breast cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:438–451. - PubMed
-
- Gennari A, André F, Barrios CH, et al. ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for the diagnosis, staging and treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2021;32:1475–1495. - PubMed
-
- https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/218197s000lbl.pdf AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP: TRUQAP™ (capivasertib). Prescribing information, 2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

