High expression of small nucleolar host gene RNA may predict poor prognosis of Hepatocellular carcinoma, based on systematic reviews and meta-analyses
- PMID: 39237890
- PMCID: PMC11378458
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12590-2
High expression of small nucleolar host gene RNA may predict poor prognosis of Hepatocellular carcinoma, based on systematic reviews and meta-analyses
Abstract
Background: The prognosis of patients with hepatocellular cancer is substantially correlated with the abnormal expression of growing long non-coding RNA small nucleolar host gene RNA (SNHG) families in liver cancer tissues. This study aimed to examine the relationship between SNHG expression and liver cancer prognosis.
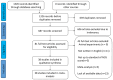
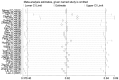
Methods: After searching six internet databases, pertinent manuscripts were found based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. To determine whether SNHG expression levels affect liver cancer prognosis, raw data were collected and hazard ratios (HRs) and odds ratios (ORs) were calculated. The results were examined for potential publication bias using the sensitivity analysis and Beeg's test.
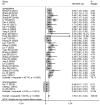
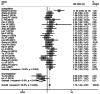
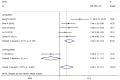
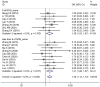
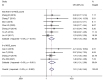
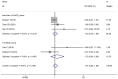
Results: Most SNHG family members were up-regulated in liver cancer tissues. High SNHG expression predicts poor liver cancer outcomes of, including overall survival (OS) (HR: 1.697, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.373-2.021), especially SNHG5 (the HR of OS is 4.74, 95%CI range from 1.35 to 6.64), progression-free survival (HR: 1.85, 95% CI: 1.25-2.73), tumor, node, metastasis (TNM) stage (OR: 1.696, 95% CI: 1.436-2.005), lymph node metastasis (OR: 2.383, 95% CI: 1.098-5.173), and tumor size (OR: 1363, 95% CI: 1.165-1.595). The OS results were found to be reliable and robust, as indicated by the sensitivity analysis. Additionally, Beeg's test demonstrated the absence of any potential publication bias for each result.
Conclusion: In liver cancer tissues, most SNHGs are highly expressed, which may signal poor prognosis. SNHG has the potential to be an intriguing predictive marker and a prospective therapeutic target for liver cancer.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Meta-analysis; Prognosis; SNHG; lncRNA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

