GSH-responsive polymeric micelles-based augmented photoimmunotherapy synergized with PD-1 blockade for eliciting robust antitumor immunity against colon tumor
- PMID: 39238020
- PMCID: PMC11378416
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-02813-w
GSH-responsive polymeric micelles-based augmented photoimmunotherapy synergized with PD-1 blockade for eliciting robust antitumor immunity against colon tumor
Erratum in
-
Correction: GSH-responsive polymeric micelles-based augmented photoimmunotherapy synergized with PD-1 blockade for eliciting robust antitumor immunity against colon tumor.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Oct 15;22(1):624. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02899-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39402676 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
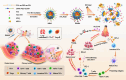
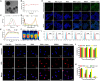
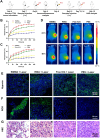
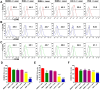
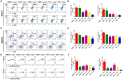
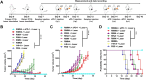
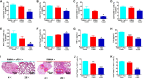
Phototherapy is a promising antitumor modality, which consists of photothermal therapy (PTT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT). However, the efficacy of phototherapy is dramatically hampered by local hypoxia in tumors, overexpression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) and programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) on tumor cells. To address these issues, self-assembled multifunctional polymeric micelles (RIMNA) were developed to co-deliver photosensitizer indocyanine green (ICG), oxygenator MnO2, IDO inhibitor NLG919, and toll-like receptor 4 agonist monophosphoryl lipid A (MPLA). It is worth noting that RIMNA polymeric micelles had good stability, uniform morphology, superior biocompatibility, and intensified PTT/PDT effect. What's more, RIMNA-mediated IDO inhibition combined with programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1)/PD-L1 blockade considerably improved immunosuppression and promoted immune activation. RIMNA-based photoimmunotherapy synergized with PD-1 antibody could remarkably inhibit primary tumor proliferation, as well as stimulate the immunity to greatly suppress lung metastasis and distant tumor growth. This study offers an efficient method to reinforce the efficacy of phototherapy and alleviate immunosuppression, thereby bringing clinical benefits to cancer treatment.
Keywords: Hypoxic tumor microenvironment; Immune checkpoint inhibitor; Immunotherapy; Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO); Phototherapy; Polymeric micelles.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Liu Q, Duo Y, Fu J, Qiu M, Sun Z, Adah D, Kang J, Xie Z, Fan T, Bao S, et al. Nano-immunotherapy: unique mechanisms of nanomaterials in Synergizing Cancer Immunotherapy. Nano Today. 2021;36:101023. - DOI
-
- Huang C, Wang H, Yang X, Yu Q, Wang H, Zhang L, Zhao Y, Zhu D. Cascade Carrier-Free nanoparticles forming in situ nanovaccines for synergistic Photothermal‐Immunotherapy of Cancer. Adv Funct Mater. 2024;34:2401489. - DOI
-
- Huang C, Zhang L, Guo Q, Zuo Y, Wang N, Wang H, Kong D, Zhu D, Zhang L. Robust Nanovaccine based on polydopamine-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for effective Photothermal‐Immunotherapy against Melanoma. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31:2010637. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

