Investigating the effects of Ginkgo biloba leaf extract on cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 39238068
- PMCID: PMC11377177
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.14914
Investigating the effects of Ginkgo biloba leaf extract on cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Aims: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder with limited treatment options. This study aimed to investigate the therapeutic effects of Ginkgo biloba leaf extract (GBE) on AD and explore its potential mechanisms of action.
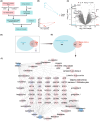
Methods: Key chemical components of GBE, including quercetin, luteolin, and kaempferol, were identified using network pharmacology methods. Bioinformatics analysis revealed their potential roles in AD through modulation of the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway.
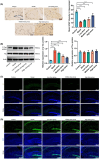
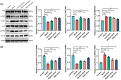
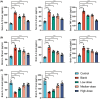
Results: Mouse experiments demonstrated that GBE improved cognitive function, enhanced neuronal morphology, and reduced serum inflammatory factors. Additionally, GBE modulated the expression of relevant proteins and mRNA.
Conclusion: GBE shows promise as a potential treatment for AD. Its beneficial effects on cognitive function, neuronal morphology, and inflammation may be attributed to its modulation of the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway. These findings provide experimental evidence for the application of Ginkgo biloba leaf in AD treatment and highlight its potential mechanisms of action.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Ginkgo biloba leaf extract; PI3K/AKT/NF‐κB signaling pathway; kaempferol; luteolin; quercetin.
© 2024 The Author(s). CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

