Hydrogel Microneedle Patches Loaded with Stem Cell Mitochondria-Enriched Microvesicles Boost the Chronic Wound Healing
- PMID: 39238258
- PMCID: PMC11447894
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.4c06921
Hydrogel Microneedle Patches Loaded with Stem Cell Mitochondria-Enriched Microvesicles Boost the Chronic Wound Healing
Abstract
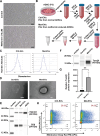
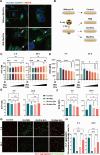
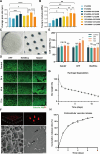
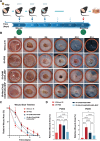
Rescuing or compensating mitochondrial function represents a promising therapeutic avenue for radiation-induced chronic wounds. Adult stem cell efficacies are primarily dependent on the paracrine secretion of mitochondria-containing extracellular vesicles (EVs). However, effective therapeutic strategies addressing the quantity of mitochondria and mitochondria-delivery system are lacking. Thus, in this study, we aimed to design an effective hydrogel microneedle patch (MNP) loaded with stem cell-derived mitochondria-rich EVs to gradually release and deliver mitochondria into the wound tissues and boost wound healing. We, first, used metformin to enhance mitochondrial biogenesis and thereby increasing the secretion of mitochondria-containing EVs (termed "Met-EVs") in adipose-derived stem cells. To verify the therapeutic effects of Met-EVs, we established an in vitro and an in vivo model of X-ray-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. The Met-EVs ameliorated the mitochondrial dysfunction by rescuing mitochondrial membrane potential, increasing adenosine 5'-triphosphate levels, and decreasing reactive oxygen species production by transferring active mitochondria. To sustain the release of EVs into damaged tissues, we constructed a Met-EVs@Decellularized Adipose Matrix (DAM)/Hyaluronic Acid Methacrylic Acid (HAMA)-MNP. Met-EVs@DAM/HAMA-MNP can load and gradually release Met-EVs and their contained mitochondria into wound tissues to alleviate mitochondrial dysfunction. Moreover, we found Met-EVs@DAM/HAMA-MNP can markedly promote macrophage polarization toward the M2 subtype with anti-inflammatory and regenerative functions, which can, in turn, enhance the healing process in mice with skin wounds combined radiation injuries. Collectively, we successfully fabricated a delivery system for EVs, Met-EVs@DAM/HAMA-MNP, to effectively deliver stem cell-derived mitochondria-rich EVs. The effectiveness of this system has been demonstrated, holding great potential for chronic wound treatments in clinic.
Keywords: hydrogel microneedle patch; metformin; mitochondria-enriched extracellular vesicle; radiation-induced injury; stem cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

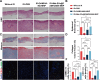
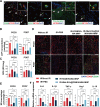

References
-
- Behroozian T.; Bonomo P.; Patel P.; Kanee L.; Finkelstein S.; van den Hurk C.; Chow E.; Wolf J. R.; Behroozian T.; Bonomo P.; et al. Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer (MASCC) Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Acute Radiation Dermatitis: International Delphi Consensus-Based Recommendations. Lancet Oncol 2023, 24, e172–e185. 10.1016/s1470-2045(23)00067-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lintel H.; Abbas D. B.; Lavin C. V.; Griffin M.; Guo J. L.; Guardino N.; Churukian A.; Gurtner G. C.; Momeni A.; Longaker M. T.; Wan D. C. Transdermal Deferoxamine Administration Improves Excisional Wound Healing in Chronically Irradiated Murine Skin. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 274. 10.1186/s12967-022-03479-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang Z.; Chen Z.; Jiang Z.; Luo P.; Liu L.; Huang Y.; Wang H.; Wang Y.; Long L.; Tan X.; Liu D.; Jin T.; Wang Y.; Wang Y.; Liao F.; Zhang C.; Chen L.; Gan Y.; Liu Y.; Yang F.; et al. Cordycepin Prevents Radiation Ulcer by Inhibiting Cell Senescence via NRF2 and AMPK in Rodents. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2538. 10.1038/s41467-019-10386-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yu C. Y.; Xu H.; Ji S.; Kwok R. T.; Lam J. W.; Li X.; Krishnan S.; Ding D.; Tang B. Z. Mitochondrion-Anchoring Photosensitizer with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics Synergistically Boosts the Radiosensitivity of Cancer Cells to Ionizing Radiation. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606167. 10.1002/adma.201606167. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

