Aquaporin 1 is renoprotective in septic acute kidney injury by attenuating inflammation, apoptosis and fibrosis through inhibition of P53 expression
- PMID: 39238634
- PMCID: PMC11374652
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1443108
Aquaporin 1 is renoprotective in septic acute kidney injury by attenuating inflammation, apoptosis and fibrosis through inhibition of P53 expression
Abstract
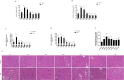
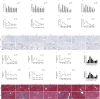
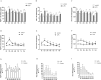
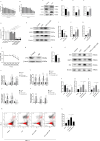
Sepsis associated Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common clinical syndrome characterized by suddenly decreased in renal function and urinary volume. This study was designed to investigate the role of Aquaporin 1 (AQP1) and P53 in the development of sepsis-induced AKI and their potential regulatory mechanisms. Firstly, transcriptome sequencing analysis of mice kidney showed AQP1 expression was reduced and P53 expression was elevated in Cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced AKI compared with controls. Bioinformatics confirmed that AQP1 expression was remarkably decreased and P53 expression was obviously elevated in renal tissues or peripheral blood of septic AKI patients. Moreover, we found in vivo experiments that AQP1 mRNA levels were dramatically decreased and P53 mRNA significantly increased following the increased expression of inflammation, apoptosis, fibrosis, NGAL and KIM-1 at various periods in septic AKI. Meanwhile, AQP1 and P53 protein levels increased significantly first and then decreased gradually in kidney tissue and serum of rats in different stages of septic AKI. Most importantly, in vivo and vitro experiments demonstrated that silencing of AQP1 greatly exacerbates renal or cellular injury by up-regulating P53 expression promoting inflammatory response, apoptosis and fibrosis. Overexpression of AQP1 prevented the elevation of inflammation, apoptosis and fibrosis by down-regulating P53 expression in Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced AKI or HK-2 cells. Therefore, our results suggested that AQP1 plays a protective role in modulating AKI and can attenuate inflammatory response, apoptosis and fibrosis via downregulating P53 in septic AKI or LPS-induced HK-2cells. The pharmacological targeting of AQP1 mediated P53 expression might be identified as potential targets for the early treatment of septic AKI.
Keywords: AKI; apoptosis; aquaporin 1; inflammation; p53; sepsis.
Copyright © 2024 Lv, Liao, Li, Liu, Luo, Diao, Wang and Jin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

