Use of Janus kinase inhibitors before and after European Medicines Agency safety recommendations: a retrospective study
- PMID: 39238648
- PMCID: PMC11374631
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1445680
Use of Janus kinase inhibitors before and after European Medicines Agency safety recommendations: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Safety recommendations for Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) issued by the European Medical Agency (EMA) in 2023 could potentially influence treatment patterns for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) drugs, but little is known about the impact of these recommendations in routine clinical care.
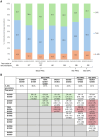
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the German RHADAR rheumatology database for adult patients with RA and documentation of a new therapy with a JAKi, tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi), or interleukin-6 receptor inhibitor (IL-6Ri). Data were grouped into half-yearly intervals from quarter (Q)2/2020 to Q3/2023. The period from Q4/2022 to Q1/2023 immediately followed the initial EMA endorsement of Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) recommendations and Q2/2023-Q3/2023 immediately followed the direct healthcare provider communication (DHPC) containing the new safety JAKi recommendations.
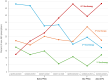
Results: Between April 1, 2020 and September 23, 2023, 3008 newly initiated therapies for TNFi (1499 [49.8%]), JAKi (1126 [37.4%]), and IL-6Ri (383 [12.7%]) were documented by the treating physicians. JAKi were increasingly used in the first two half-year periods (from 29.7% of these therapies in Q2/2020-Q3/2020 to 46.7% in Q2/2021-Q3/2021; odds ratio [OR] 2.08; p<0.001). The proportion of initiated JAKi therapies decreased significantly after the PRAC recommendations (32.9%; OR vs peak 0.56; p=0.001) and the DHPC letter (26.1%; OR vs peak 0.40; p<0.001). JAKi were more likely to be used as >3rd-line therapy in later time periods.
Conclusions: This exploratory study suggests that EMA safety recommendations for JAKi influenced treatment patterns of RA patients who received JAKi in Germany. Additional studies will be needed to confirm these findings.
Keywords: cancer; interleukin-6 receptor inhibitors; major adverse cardiac event; oral surveillance; rheumatoid arthritis; treatment; tumor necrosis factor inhibitors; venous thromboembolism.
Copyright © 2024 Strunz, Risser, Englbrecht, Witte, Froehlich, Schmalzing, Gernert, Hueper, Bartz-Bazzanella, von der Decken, Karberg, Gauler, Späthling-Mestekemper, Kuhn, Vorbrüggen, Welcker and Kleinert.
Conflict of interest statement
P-PS received research funding from Chugai and speaker’s fees or travel grants from AbbVie, Boehringer/Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, and Janssen-Cilag. LR received travel/meeting support from AbbVie and Biocon Biologics Germany. ME received funding for the present study for data analysis from RHADAR GbR and also received consulting fees from AbbVie and RHADAR, speaker’s fees from AbbVie, Janssen-Cilag, Sanofi, and Swedish Orphan Biovitrum, and is on the advisory board of Chugai Pharma Germany. TW received consulting and/or speaker’s fees from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai, Fresenius Kabi, Galapagos, GSK, Janssen, Lilly, Medac, Nordic, Novartis, Sanofi, and UCB and travel/meeting support from AbbVie, Janssen, Lilly, and UCB. MF received consulting fees or travel/meeting support from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Janssen, Hexal, Pfizer, Takeda, and UCB. MS received research grants from Chugai and Novartis, consulting and/or speaker’s fees from AbbVie, Alfasigma/Galapagos/Gilead, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BMS, Boehringer/Ingelheim, Chugai/Roche, EUSA-Pharma, Hexal/Sandoz, Janssen-Cilag, Lilly, Novartis, onkowissen.de, and UCB, travel/meeting support from Alfasigma/Galapagos, Boehringer/Ingelheim, Celgene, Chugai/Roche, Medac, Mylan, and UCB, participates on advisory boards for AbbVie, Alfasigma/Galapagos/Gilead, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer/Ingelheim, Chugai/Roche, EUSA-Pharma, Hexal/Sandoz, Janssen-Cilag, Lilly, Novartis, onkowissen.de, and UCB, and has a leadership role in the Deutsches Netzwerk Systemische Sklerodermie DNSS. MG receive grants from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, and Pfizer, consulting fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Novartis, and Takeda, speaker’s fees from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen, and Novartis, and travel/meeting support from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and UCB. SH received speaker’s fees from AbbVie and travel/meeting support from Janssen-Cilag and UCB. PB-B received speaker’s fees from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai/Roche, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB and travel/meeting support from AbbVie. CV received travel/meeting support from AbbVie and Galapagos/Alpha sigma. KK received speaker’s fees from AbbVie, Galapagos, Novartis, Rheumakademie, and UCB and travel/meeting support from UCB. GG received speaker’s fees from AbbVie, Galapagos, and Novartis and travel/meeting support from AbbVie and Novartis. SS-M received speakers fees from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, GSK, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and UCB. WV received travel support from Bundesverband Managed Care. MW received consulting and/or speaker’s fees from AbbVie, Fresenius, Galapagos, Lilly, and UCB and travel/meeting support from AbbVie, Galapagos, GSK, Lilly, and UCB. SK received grants from AbbVie, Novartis, and Sparrow, and consulting and/or speaker’s fees from AbbVie, Celgene, Chugai, Galapagos, Novartis, and Siemens Healthineers. PB-B, CvdD, KK, GG, SS-M, CK, WV, MW, and SK are members of RheumaDatenRhePort RHADAR GbR.
Figures
References
-
- European Medicines Agency . EMA confirms measures to minimize risk of serious side effects with Janus kinase inhibitors for chronic inflammatory disorders (2022). Available online at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/ema-confirms-measures-minimise-risk-se... (Accessed 8 April 2024).
-
- European Medicines Agency . Cibinqo (abrocitinib), Jyseleca (filgotinib), Olumiant (baricitinib), Rinvoq (Upadacitinib) and Xeljanz (tofacitinb) — Updated recommendations to minimize the risks of Malignancy, major adverse cardiovascular events, serious infections, venous thromboembolism and mortality with use of Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) (2023). Available online at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/dhpc/direct-healthcare-profession... (Accessed 8 April 2024).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

