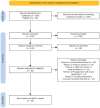
The Impact of Infectious Diseases on Psychiatric Disorders: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39238736
- PMCID: PMC11377121
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.66323
The Impact of Infectious Diseases on Psychiatric Disorders: A Systematic Review
Abstract
The complex connection between some infectious illnesses and some psychiatric disorders is an important area of study, with infections known to cause a diverse range of psychiatric symptoms. This association poses significant challenges for physicians in differentiating between mental illnesses induced by infections and those stemming from underlying psychiatric conditions. This study systematically synthesizes literature from various databases that explain the relationship between certain infectious diseases and specific psychiatric disorders. The systematic review explores mechanisms such as neuroinflammation, direct central nervous system (CNS) infection, and the interaction between the immune system and psychiatric conditions. The study examines various infectious pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, parasites, prion diseases, and fungi. An analysis of these findings is presented in the study's discussion section, along with a review of therapeutic methods such as drug use and psychological treatment. The review emphasizes the need for multidisciplinary teamwork and thorough clinical examinations in managing psychiatric symptoms caused by infections. It also highlights the significant role of public health measures in mitigating the impact of psychiatric diseases related to infectious illnesses. The study finds that current therapeutic methods include pharmacological and psychological treatments, which can effectively manage these conditions. The study has concluded that psychiatric manifestations are prevalent across various infectious diseases, including those caused by viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi. Key mechanisms identified include neuroinflammation, direct infection of the CNS, and the immuno-psychiatric interface, all of which contribute to the development of psychiatric symptoms. The future of managing these complex conditions lies in a comprehensive approach that combines clinical, therapeutic, and public health strategies.
Keywords: cns infection; immuno-psychiatric interface; infectious diseases; neuroinflammation; psychiatric disorders.
Copyright © 2024, Okobi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neurological Manifestations of Infectious Diseases: Insights From Recent Cases.Cureus. 2023 Dec 28;15(12):e51256. doi: 10.7759/cureus.51256. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. Retraction in: Cureus. 2025 Jan 16;17(1):r160. doi: 10.7759/cureus.r160. PMID: 38288186 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
Post-Infectious Autoimmunity in the Central (CNS) and Peripheral (PNS) Nervous Systems: An African Perspective.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 9;13:833548. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.833548. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35356001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Multidisciplinary Approaches to Comorbid Psychiatric and Medical Disorders: A Scoping Review.Life (Basel). 2025 Feb 6;15(2):251. doi: 10.3390/life15020251. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40003660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Brain-Heart Axis: An Umbrella Review on Impact of Psychiatric Disease on Incidence, Management, and Outlook of Cardiovascular Disease.Life (Basel). 2024 Jul 23;14(8):919. doi: 10.3390/life14080919. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D as a Modulator of Neuroinflammation: Implications for Brain Health.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(5):323-332. doi: 10.2174/0113816128281314231219113942. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38303529 Review.
Cited by
-
Case Report: The intersection of psychiatry and medicine: diagnostic and ethical insights from case studies.Front Psychiatry. 2025 Apr 22;16:1576179. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1576179. eCollection 2025. Front Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40330647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Does preregistration improve the credibility of research findings? Rubin M. Quant Meth Psych. 2020;16:376–390.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources