Effectiveness of remote ischemic preconditioning in patients undergoing transplant surgery: meta-analysis of randomized control studies
- PMID: 39238974
- PMCID: PMC11374220
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002306
Effectiveness of remote ischemic preconditioning in patients undergoing transplant surgery: meta-analysis of randomized control studies
Abstract
Introduction: Remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPC) is a phenomenon in which the induction of shortened periods of ischemia prior to surgical procedures within a distant tissue preserves other tissues or organs of concern, such as the liver or kidney in transplant surgery, in the event of prolonged ischemic insults. The authors aim to evaluate the effectiveness of RIPC in patients undergoing transplant surgery, specifically kidney and liver transplants.
Materials and methods: PubMed, Embase, and Scopus were searched until 19 December 2023 for trials evaluating RIPC in patients undergoing transplant surgery. A total of 9364 search articles were obtained, which yielded 10 eligible studies. Data analysis was done using RevMan 5.4 software. The risk of bias was done using Cochrane risk of bias tool.
Results and discussion: For graft rejection, the study observed a relative risk of 0.99 (95% CI, 0.49-1.98, P=0.97) from 5 trials, indicating no significant effect of RIPC on graft survival in both kidney and liver transplants. The length of hospital stay also showed no significant decrease for those undergoing RIPC, with mean difference (MD) of -0.58 (95% CI, -1.38 to 0.23, P=0.16). GFR at 1-year post-kidney transplant did not significantly change in the RIPC group compared to controls, as evidenced by an MD of -0.13 (95% CI, -3.79 to 3.54, P=0.95). These results collectively suggest that RIPC may not be effective in reducing patient, or graft, outcomes.
Keywords: RIC; RIPC; kidney transplant; organ transplantation; remote ischemic preconditioning; transplant.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors involved in this review certify that they have no conflict of interest, affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest.Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures
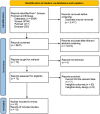


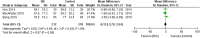
References
-
- Przyklenk K, Whittaker P. Remote ischemic preconditioning: current knowledge, unresolved questions, and future priorities. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther 2011;16:255–259. - PubMed
-
- Karuppasamy P, Chaubey S, Dew T, et al. . Remote intermittent ischemia before coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a strategy to reduce injury and inflammation? Basic Res Cardiol 2011;106:511–519. - PubMed
-
- Gajardo AIJ, Karachon L, Bustamante P, et al. . Autonomic imbalance in cardiac surgery: a potential determinant of the failure in remote ischemic preconditioning. Med Hypotheses 2018;118:146–150. - PubMed
-
- Costa FL, Teixeira RK, Yamaki VN, et al. . Remote ischemic conditioning temporarily improves antioxidant defense. J Surg Res 2016;200:105–109. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
