An update on technical and safety practice patterns of interlaminar epidural steroid injections
- PMID: 39239216
- PMCID: PMC11373040
- DOI: 10.1016/j.inpm.2023.100371
An update on technical and safety practice patterns of interlaminar epidural steroid injections
Abstract
Introduction: Interlaminar epidural steroid injections (ILESIs) are mainstay in the management of low back, neck and radicular pain and are a commonly performed pain management procedure in the United States. Our survey aims to provide an update in practice patterns of ILESIs among interventional pain physicians.
Methods: We distributed a 91-item survey nationwide to private and academic interventional pain physicians who perform epidural steroid injections (ESIs). The survey was distributed via REDCap with a series of questions inquiring about current practices in epidural steroid injections from March 2021 to March 2022. Cross sectional data from survey responses specific to ILESI-related practices were captured and synthesized.
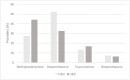
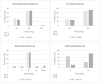
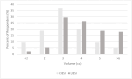
Results: Of 103 complete survey responses, 96 physicians perform ILESIs (cervical, 87.5 %; thoracic, 82.3 %; lumbar 99 %). Nearly all surveyed physicians utilize fluoroscopy (98.1 %) over other modalities like MRI and ultrasound. For CIESIs, dexamethasone was the preferred steroid (52.4 %) over methylprednisolone (23.7 %); the converse was true for LIESIs in which methylprednisolone (44.2 %) was preferred over dexamethasone (32.6 %). The majority of providers performing ILESI's (91.7 %) preferred a Tuohy/Weiss needle while only a small fraction preferred the Quincke needle (7.2 %). Sedation practices were more varied with only about half of providers (47.6 %) offering medications. Furthermore, a great fraction of providers continue to use contrast for LIESIs (97.9 %) and CIESIs (89.6 %).
Discussion: Our survey suggests that despite updated consensus recommendations, variability continues to exist in procedural practice patterns. Highlighting areas of variable adherence to current safety guidelines can assist with what is emphasized in the generation of future evidence-based guidelines. Though our survey was conducted in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic with resultant supply chain shortages, more research is needed to elucidate what variables may factor into why proceduralists may stray from guideline concordant care.
Keywords: Back pain; Epidural steroid injections; Interlaminar epidural steroid injections; Interventional pain procedures; Pain medicine.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Variations in Interlaminar Epidural Steroid Injection Practice Patterns by Interventional Pain Management Physicians in the United States.Pain Physician. 2018 Sep;21(5):E493-E499. Pain Physician. 2018. PMID: 30282397
-
Current Trends in Steroid Dose Choice and Frequency of Administration of Epidural Steroid Injections: A Survey Study.PM R. 2020 Jan;12(1):49-54. doi: 10.1002/pmrj.12192. Epub 2019 Sep 11. PM R. 2020. PMID: 31119858
-
An update on technical and safety practice patterns in transforaminal epidural steroid injections.Interv Pain Med. 2023 Oct 18;2(4):100286. doi: 10.1016/j.inpm.2023.100286. eCollection 2023 Dec. Interv Pain Med. 2023. PMID: 39239222 Free PMC article.
-
Epidural Interventions in the Management of Chronic Spinal Pain: American Society of Interventional Pain Physicians (ASIPP) Comprehensive Evidence-Based Guidelines.Pain Physician. 2021 Jan;24(S1):S27-S208. Pain Physician. 2021. PMID: 33492918 Review.
-
Image Guidance Technologies for Interventional Pain Procedures: Ultrasound, Fluoroscopy, and CT.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2018 Jan 26;22(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s11916-018-0660-1. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2018. PMID: 29374352 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the effectiveness of interlaminar epidural steroid injections for cervical radiculopathy using PROMIS as an outcome measure.Interv Pain Med. 2024 Dec 5;3(4):100528. doi: 10.1016/j.inpm.2024.100528. eCollection 2024 Dec. Interv Pain Med. 2024. PMID: 39717451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation; 2020. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries.https://www.healthdata.org/research-article/global-burden-369-diseases-a... (1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019). [Internet] [cited 2023 Feb 20]. Available from:
-
- Sharma A.K., Vorobeychik Y., Wasserman R., Jameson J., Moradian M., Duszynski B., et al. The effectiveness and risks of fluoroscopically guided lumbar interlaminar epidural steroid injections: a systematic review with comprehensive analysis of the published data. Pain Med. 2017;18(2):239–251. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

