Toward a large-batch manufacturing process for silicon-stabilized lipid nanoparticles: A highly customizable RNA delivery platform
- PMID: 39239259
- PMCID: PMC11374960
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101299
Toward a large-batch manufacturing process for silicon-stabilized lipid nanoparticles: A highly customizable RNA delivery platform
Abstract
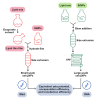
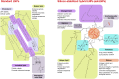
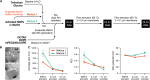
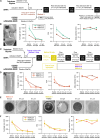
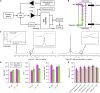
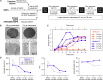
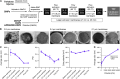
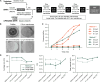
While lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are a key enabling technology for RNA-based therapeutics, some outstanding challenges hinder their wider clinical translation and use, particularly in terms of RNA stability and limited shelf life. In response to these limitations, we developed silicon-stabilized hybrid lipid nanoparticles (sshLNPs) as a next-generation nanocarrier with improved physical and temperature stability, as well as the highly advantageous capacity for "post-hoc loading" of RNA. Nevertheless, previously reported sshLNP formulations were produced using lipid thin film hydration, making scale-up impractical. To realize the potential of this emerging delivery platform, a manufacturing process enabling multikilogram batch sizes was required for successful clinical translation and deployment at scale. This was achieved by developing a revised protocol based on solvent injection mixing and incorporating other process adjustments to enable in-flow extrusion of multiliter volumes, while ensuring sshLNPs with the desired characteristics. Optimized procedures for nanoparticle formation, extrusion, and tangential flow filtration (to remove residual organic solvent) currently enable production of 2 kg finished batches. Importantly, sshLNPs produced via the modified large-scale workflow show equivalent physical and functional properties to those derived from the earlier small-scale methods, paving the way for GMP manufacturing protocols to enable vital translational clinical studies.
Keywords: Bio-Courier; RNA delivery; gene therapy; lipid nanoparticles; process development; silicon nanoparticles; sshLNP.
Crown Copyright © 2024 Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employees of SiSaf Ltd. S.S.-S. is CEO, board member, and shareholder of SiSaf Ltd. S.S.-S., N.T.-P., and A.D. are named inventors in a patent application filed by SiSaf Ltd. on the manufacturing process for silicon-stabilized lipid nanoparticles.
Figures
References
-
- Moss K.H., Popova P., Hadrup S.R., Astakhova K., Taskova M. Lipid nanoparticles for delivery of therapeutic RNA oligonucleotides. Mol. Pharm. 2019;16:2265–2277. - PubMed
-
- Verma M., Ozer I., Xie W., Gallagher R., Teixeira A., Choy M. The landscape for lipid-nanoparticle-based genomic medicines. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023;22:349–350. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

