Efficacy and safety of PD-1 inhibitors plus anti-angiogenesis tyrosine kinase inhibitors with or without transarterial chemo(embolization) for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 39239275
- PMCID: PMC11374639
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1364345
Efficacy and safety of PD-1 inhibitors plus anti-angiogenesis tyrosine kinase inhibitors with or without transarterial chemo(embolization) for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The triple combination of programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) inhibitors plus anti-angiogenesis tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) with or without transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) or hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) enhance the effect of treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC). The present study compared the efficacy and safety of PD-1 plus TKI with or without transarterial chemo(embolization) for uHCC.
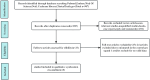
Methods: The meta-analysis was conducted using data acquired from PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, Ovid, Web of Science, and Clinical Trials.gov from the inception date to December 2023. All clinical outcomes of interest included overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR), and adverse events (AEs). The hazard ratio (HR) and risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were used to measure the pooled effect. In addition, subgroup analysis was conducted to determine the specific patient population that benefited.
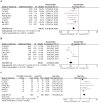
Results: The OS (HR = 0.47; 95% CI: 0.39-0.56, P < 0.05), PFS (HR = 0.52; 95% CI: 0.45-0.60, P < 0.05), and ORR (RR = 1.94; 95% CI: 1.60-2.35, P < 0.05) were significantly better in TACE/HAIC+TKI+PD-1(TACE/HAIC TP) group than TKI+PD-1(TP) group. The incidence of AEs was acceptable.
Conclusion: The triple therapy of TACE/HAIC TP had better efficacy for uHCC than TP, with acceptable security.
Systematic review registration: PROSPERO, identifier CRD42023475953.
Keywords: PD-1 inhibitors; hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy; transarterial chemoembolization; tyrosine kinase inhibitors; unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.
Copyright © 2024 Chen, Jia, Li, Cui, Wang, Zhang, Bian and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Significance of Transarterial Chemo(Embolization) Combined With Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Era of Systemic Therapy: A Systematic Review.Front Immunol. 2022 May 23;13:913464. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.913464. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35677059 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Effectiveness and Safety of Transarterial Chemoembolization: Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy Plus Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors With or Without Programmed Cell Death Protein-1 Inhibitors for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma-A Retrospective Study.Ann Surg Oncol. 2024 Nov;31(12):7860-7869. doi: 10.1245/s10434-024-15933-2. Epub 2024 Aug 1. Ann Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39090499
-
Efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization plus lenvatinib combined with PD-1 inhibitors versus transarterial chemoembolization plus lenvatinib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 30;15:1466113. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1466113. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39281676 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Plus Anti-PD-1 Antibodies with Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy or Transarterial Chemoembolization for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023 Oct 6;10:1735-1748. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S431917. eCollection 2023. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023. PMID: 37822726 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced antitumor activity of combined hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy with Lenvatinib and PD-1 inhibitors in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 12;15:1513394. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1513394. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40012555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Department of Medical Administration. National Health and Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China . Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer in China (2019 edition). Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. (2020) 28:112–28. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2020.02.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- He MK, Le Y, Li QJ, Yu ZS, Li SH, Wei W, et al. . Hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy using mFOLFOX versus transarterial chemoembolization for massive unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective non-randomized study. Chin J Cancer. (2017) 36:83. doi: 10.1186/s40880-017-0251-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

