Comparative Evaluation of Honey Versus Alcohol as a Fixative in Cytological Samples: An Institutional Study
- PMID: 39239318
- PMCID: PMC11373716
- DOI: 10.4103/joc.joc_182_23
Comparative Evaluation of Honey Versus Alcohol as a Fixative in Cytological Samples: An Institutional Study
Abstract
Introduction: Fixation plays an important role in fixing the cells, making them amenable for evaluation. Ethanol (95%) has been used as a standard cytological fixative. Honey can be introduced as a natural fixative.
Objectives: 1. To study cytomorphological features of smears fixed in 20% unprocessed honey. 2. To study the efficacy of honey as a fixative when compared with ethanol in both hematoxylin and eosin (H and E) stain and Papanicolaou (PAP) stain for cytological samples.
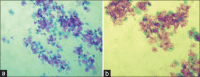
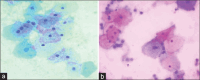
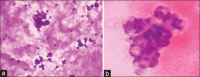
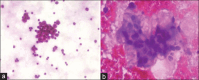
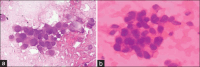
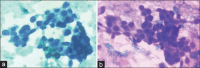
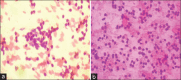
Materials and methods: A cross-sectional study was done in the Department of Pathology for 2 months on 100 cytological samples consisting of body fluids (peritoneal and pleural), cervical smears, and FNACs. These smears were fixed separately in 95% ethanol and 20% unprocessed honey for 5 minutes and were stained with both PAP and H and E stain. The cytomorphologies of both the smears were compared based on five parameters, clarity of staining, uniformity of staining, overall morphology, nuclear details, and cytoplasmic details, and the final score was calculated by adding all the scores: Total Score ≤2, poor score; 3-4, good score; 5, excellent score.
Results: Cervical smears fixed in honey showed similar features to ethanol-fixed smears. Fluid smears fixed in honey and stained with PAP yielded superior results compared to those stained with H and E, as shown by a kappa value of 0.259. However, neither of the smears demonstrated statistical significance. The FNAC samples stained with H and E and PAP exhibited nearly identical results, with a kappa value of 0.688 and 0.647, respectively. FNAC and PAP smears were the next two most successful cytological smear types, with cervical smears exhibiting the best results of the three.
Conclusion: In honey-fixed smears, we can easily observe all cellular features with clarity. It enhances safety and the working environment in the laboratory. Honey can serve as an effective substitute in situations where resources are limited.
Keywords: Alcohol; cytology fixatives; honey.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Cytology | Indian Academy of Cytologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Nil.
Figures

References
-
- Nerune SM, Khan MN, Potekar RM, Patil V. Natural versus synthetic fixative in oral cytological smears-A double blind study. Indian J Pathol Oncol. 2018;5:663–6.
-
- Ishaq R, Azmat H, Omair M, Sheikh AK, Tanwani AK. Comparison of honey with alcohol as a fixative in fine needle aspiration cytology. Int J Pathol. 2017;15:15–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
