Single-cell RNA sequencing highlights the immunosuppression of IDO1+ macrophages in the malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia
- PMID: 39239507
- PMCID: PMC11373622
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.99112
Single-cell RNA sequencing highlights the immunosuppression of IDO1+ macrophages in the malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia
Abstract
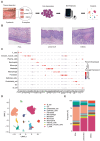
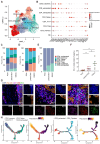
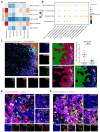
Rationale: Immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (iTME) plays an important role in carcinogenesis, and some macrophage subsets are associated with iTME generation. However, the sub-population characterization of macrophages in oral carcinogenesis remains largely unclear. Here, we investigated the immunosuppressive status with focus on function of a macrophage subset that expressed indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase 1 (Macro-IDO1) in oral carcinogenesis. Methods: We built a single cell transcriptome atlas from 3 patients simultaneously containing oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), precancerous oral leukoplakia (preca-OLK) and paracancerous tissue (PCA). Through single-cell RNA sequencing and further validation using multicolor immunofluorescence staining and the in vitro/in vivo experiments, the immunosuppressive cell profiles were built and the role of a macrophage subset that expressed indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase 1 (Macro-IDO1) in the malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia was evaluated. Results: The iTME formed at preca-OLK stage, as evidenced by increased exhausted T cells, Tregs and some special subsets of macrophages and fibroblasts. Macro-IDO1 was predominantly enriched in preca-OLK and OSCC, distributed near exhausted T cells and possessed tumor associated macrophage transformation potentials. Functional analysis revealed the established immunosuppressive role of Macro-IDO1 in preca-OLK and OSCC: enriching the immunosuppression related genes; having an established level of immune checkpoint score; exerting strong immunosuppressive interaction with T cells; positively correlating with the CD8-exhausted. The immunosuppression related gene expression of macrophages also increased in preca-OLK/OSCC compared to PCA. The use of the IDO1 inhibitor reduced 4NQO induced oral carcinogenesis in mice. Mechanistically, IFN-γ-JAK-STAT pathway was associated with IDO1 upregulation in OLK and OSCC. Conclusions: These results highlight that Macro-IDO1-enriched in preca-OLK possesses a strong immunosuppressive role and contributes to oral carcinogenesis, providing a potential target for preventing precancerous legions from transformation into OSCC.
Keywords: 3-dioxygenase 1.; Oral leukoplakia; Oral squamous cell carcinoma; immunosuppressive microenvironment; indoleamine 2; macrophage.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I. et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:229–263. - PubMed
-
- Mello FW, Miguel AFP, Dutra KL, Porporatti AL, Warnakulasuriya S, Guerra ENS. et al. Prevalence of oral potentially malignant disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Oral Pathol Med. 2018;47:633–40. - PubMed
-
- Warnakulasuriya S. Oral potentially malignant disorders: A comprehensive review on clinical aspects and management. Oral Oncol. 2020;102:104550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

