Clinical applications of circulating biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 39239557
- PMCID: PMC11375801
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1449232
Clinical applications of circulating biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
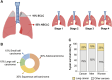
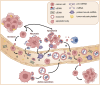
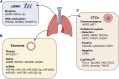
Despite recent advances in cancer diagnostics and treatment, the mortality associated with lung cancer is still the highest in the world. Late-stage diagnosis, often accompanied by metastasis, is a major contributor to the high mortality rates, emphasizing the urgent need for reliable and readily accessible diagnostic tools that can detect biomarkers unique to lung cancer. Circulating factors, such as circulating tumor DNA and extracellular vesicles, from liquid biopsy have been recognized as diagnostic or prognostic markers in lung cancer. Numerous clinical studies are currently underway to investigate the potential of circulating tumor DNA, circulating tumor RNA, exosomes, and exosomal microRNA within the context of lung cancer. Those clinical studies aim to address the poor diagnostics and limited treatment options for lung cancer, with the ultimate goal of developing clinical markers and personalized therapies. In this review, we discuss the roles of each circulating factor, its current research status, and ongoing clinical studies of circulating factors in non-small cell lung cancer. Additionally, we discuss the circulating factors specifically found in lung cancer stem cells and examine approved diagnostic assays designed to detect circulating biomarkers in lung cancer patients.
Keywords: cancer stem cells; circulating factors; ctDNA; diagnostic tools; exosome; microRNA; non-small cell lung cancer.
Copyright © 2024 Oh, Imam-Aliagan, Kim, Kim, Izaguirre, Sung and Yim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Liquid Biopsy in Lung Cancer: Clinical Applications of Circulating Biomarkers (CTCs and ctDNA).Micromachines (Basel). 2018 Feb 28;9(3):100. doi: 10.3390/mi9030100. Micromachines (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30424034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liquid biopsy: Circulating exosomal long noncoding RNAs in cancer.Clin Chim Acta. 2019 Aug;495:331-337. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.04.082. Epub 2019 May 2. Clin Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31054913 Review.
-
Clinical Utility of Liquid Diagnostic Platforms in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Oncologist. 2016 Sep;21(9):1121-30. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0082. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Oncologist. 2016. PMID: 27388233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: opportunities and challenges.Ann Oncol. 2021 Apr;32(4):466-477. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.01.074. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Ann Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33548389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current and future applications of liquid biopsy in non-small-cell lung cancer-a narrative review.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023 Mar 31;12(3):594-614. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-742. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37057121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional tumor-derived exosomes in NSCLC progression and clinical implications.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 19;16:1485661. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1485661. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40176898 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

