Unraveling the interplay: exploring signaling pathways in pancreatic cancer in the context of pancreatic embryogenesis
- PMID: 39239563
- PMCID: PMC11374643
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1461278
Unraveling the interplay: exploring signaling pathways in pancreatic cancer in the context of pancreatic embryogenesis
Abstract
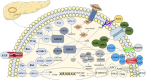
Pancreatic cancer continues to be a deadly disease because of its delayed diagnosis and aggressive tumor biology. Oncogenes and risk factors are being reported to influence the signaling pathways involved in pancreatic embryogenesis leading to pancreatic cancer genesis. Although studies using rodent models have yielded insightful information, the scarcity of human pancreatic tissue has made it difficult to comprehend how the human pancreas develops. Transcription factors like IPF1/PDX1, HLXB9, PBX1, MEIS, Islet-1, and signaling pathways, including Hedgehog, TGF-β, and Notch, are directing pancreatic organogenesis. Any derangements in the above pathways may lead to pancreatic cancer. TP53: and CDKN2A are tumor suppressor genes, and the mutations in TP53 and somatic loss of CDKN2A are the drivers of pancreatic cancer. This review clarifies the complex signaling mechanism involved in pancreatic cancer, the same signaling pathways in pancreas development, the current therapeutic approach targeting signaling molecules, and the mechanism of action of risk factors in promoting pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: embryogenesis; pancreatic cancer; signaling pathway; therapeutic approach; transcription factor.
Copyright © 2024 Swain, Narayan and Mishra.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pbx1 inactivation disrupts pancreas development and in Ipf1-deficient mice promotes diabetes mellitus.Nat Genet. 2002 Apr;30(4):430-5. doi: 10.1038/ng860. Epub 2002 Mar 25. Nat Genet. 2002. PMID: 11912494
-
Selective agenesis of the dorsal pancreas in mice lacking homeobox gene Hlxb9.Nat Genet. 1999 Sep;23(1):67-70. doi: 10.1038/12669. Nat Genet. 1999. PMID: 10471501
-
Loss of Activin Receptor Type 1B Accelerates Development of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms in Mice With Activated KRAS.Gastroenterology. 2016 Jan;150(1):218-228.e12. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.09.013. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Gastroenterology. 2016. PMID: 26408346 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and transcription factors: role of c-Myc.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2011 Jun;42(2):76-84. doi: 10.1007/s12029-011-9258-0. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21279552 Review.
-
Signaling and transcriptional control of pancreatic organogenesis.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002 Oct;12(5):540-7. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(02)00338-6. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002. PMID: 12200159 Review.
References
-
- Austen J., Bronte E. (2023). Oncogenic signaling pathways in carcinogenesis. J. Carcinog. 22 (1). 10.4103/jcar.jcar_22_01_16 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous