14-3-3σ restricts YY1 to the cytoplasm, promoting therapy resistance, and tumor progression in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 39239852
- PMCID: PMC11622004
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.35176
14-3-3σ restricts YY1 to the cytoplasm, promoting therapy resistance, and tumor progression in colorectal cancer
Abstract
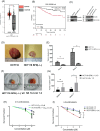
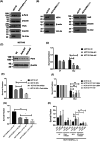
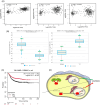
14-3-3σ functions as an oncogene in colorectal cancer and is associated with therapy resistance. However, the mechanisms underlying these observations are not clear. The results in this report demonstrate that loss of 14-3-3σ in colorectal cancer cells leads to a decrease in tumor formation and increased sensitivity to chemotherapy. The increased sensitivity to chemotherapy is due to a decrease in the expression of UPR pathway genes in the absence of 14-3-3σ. 14-3-3σ promotes expression of the UPR pathway genes by binding to the transcription factor YY1 and preventing the nuclear localization of YY1. YY1, in the absence of 14-3-3σ, shows increased nuclear localization and binds to the promoter of the UPR pathway genes, resulting in decreased gene expression. Similarly, a YY1 mutant that cannot bind to 14-3-3σ also shows increased nuclear localization and is enriched on the promoter of the UPR pathway genes. Finally, inhibition of the UPR pathway with genetic or pharmacological approaches sensitizes colon cancer cells to chemotherapy. Our results identify a novel mechanism by which 14-3-3σ promotes tumor progression and therapy resistance in colorectal cancer by maintaining UPR gene expression.
Keywords: 14‐3‐3σ; 5‐fluorouracil; colorectal cancer; unfolded protein response.
© 2024 The Author(s). International Journal of Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Briffa R, Langdon SP, Grech G, Harrison DJ. Acquired and intrinsic resistance to colorectal cancer treatment. In: Chen J, ed. Colorectal Cancer—Diagnosis, Screening and Management. Intech Open; 2018:57‐81.
-
- Kozovska Z, Gabrisova V, Kucerova L. Colon cancer: cancer stem cells markers, drug resistance and treatment. Biomed Pharmacother. 2014;68:911‐916. - PubMed
-
- Aitken A. 14‐3‐3 proteins: a historic overview. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006;16:162‐172. - PubMed
-
- Muslin AJ, Tanner JW, Allen PM, Shaw AS. Interaction of 14‐3‐3 with signaling proteins is mediated by recognition of phosphoserine. Cell. 1996;84:889‐897. - PubMed
-
- Yaffe MB, Rittinger K, Volinia S, et al. The structural basis for 14‐3‐3 phosphopeptide binding specificity. Cell. 1997;91:961‐971. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

