Impact of thoracic radiotherapy on first-line treatment outcomes in ES-SCLC patients
- PMID: 39240166
- PMCID: PMC11378358
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.70175
Impact of thoracic radiotherapy on first-line treatment outcomes in ES-SCLC patients
Abstract
Background: The therapeutic advantage of thoracic radiotherapy (tRT) as an adjunct to first-line immunotherapy and chemotherapy in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) remains unclear. We sought to elucidate this in a retrospective cohort study comparing the effectiveness and safety of tRT in combination with first-line immunotherapy and chemotherapy.
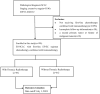
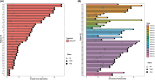
Methods: Our retrospective study included patients with ES-SCLC, treated at the West China Hospital between January 2019 and December 2022. They received first-line immunotherapy and chemotherapy and were categorized into two cohorts based on the administration of tRT. The primary outcomes were overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). Cox regression analysis was utilized to identify potential independent predictors of prognosis and to compare the treatment outcomes across various patient subgroups. Treatment-related toxicities across both cohorts were compared using the Chi-squared test.
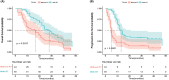
Results: A total of 99patients were eligible for the study, out of which 55 received tRT. The medianduration of follow-up was 39 months. Remarkably, patients who received tRTdemonstrated superior OS and PFS in comparison to those who did not (P < 0.05). Subgroup analysis further confirmed these findings. Multivariate analysisidentified treatment group and liver metastasis as independent prognosticfactors (P < 0.05). The incidence of grade 3-4 adverse events showed nostatistically significant difference between the two cohorts.
Conclusions: Thus, weconfirmed that the addition of tRT to the conventional regimen of first-linechemotherapy and immunotherapy yields better survival outcomes without asignificant increase in toxicity.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Extensive‐stage small cell lung cancer; Immunotherapy; Survival outcomes; Thoracic radiotherapy.
© 2024 The Author(s). Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2023HXFH020/West China Hospital of Sichuan University 2023 Clinical Research Incubation Project
- HX-H2212352/2022 Wu Jieping Medical Foundation
- 2024YFHZ0012/Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Support Program
- 2022-I2M-C&T-B-106/Clinical and Translational Medicine Research Special Programme, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

