Novel cyclic homogeneous oscillation detection method for high accuracy and specific characterization of neural dynamics
- PMID: 39240267
- PMCID: PMC11379461
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.91605
Novel cyclic homogeneous oscillation detection method for high accuracy and specific characterization of neural dynamics
Abstract
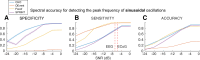
Determining the presence and frequency of neural oscillations is essential to understanding dynamic brain function. Traditional methods that detect peaks over 1/f noise within the power spectrum fail to distinguish between the fundamental frequency and harmonics of often highly non-sinusoidal neural oscillations. To overcome this limitation, we define fundamental criteria that characterize neural oscillations and introduce the cyclic homogeneous oscillation (CHO) detection method. We implemented these criteria based on an autocorrelation approach to determine an oscillation's fundamental frequency. We evaluated CHO by verifying its performance on simulated non-sinusoidal oscillatory bursts and validated its ability to determine the fundamental frequency of neural oscillations in electrocorticographic (ECoG), electroencephalographic (EEG), and stereoelectroencephalographic (SEEG) signals recorded from 27 human subjects. Our results demonstrate that CHO outperforms conventional techniques in accurately detecting oscillations. In summary, CHO demonstrates high precision and specificity in detecting neural oscillations in time and frequency domains. The method's specificity enables the detailed study of non-sinusoidal characteristics of oscillations, such as the degree of asymmetry and waveform of an oscillation. Furthermore, CHO can be applied to identify how neural oscillations govern interactions throughout the brain and to determine oscillatory biomarkers that index abnormal brain function.
Keywords: ECoG; EEG; SEEG; brain rhythm; human; neural oscillation; neuroscience.
Conflict of interest statement
HC One U.S. patent (Provisional Application Serial No.63/326,257) related to systems and methodsfor detection of neurophysiological signal oscillations described in this manuscript was filed on March 31, 2022. The inventors/contributors of this patent involve some of themanuscript authors, including HC, MA, JTW, PB, MA, JW No competing interests declared, PB One U.S. patent (Provisional Application Serial No.63/326,257) related to systems and methods
Figures



















Update of
-
Novel Cyclic Homogeneous Oscillation Detection Method for High Accuracy and Specific Characterization of Neural Dynamics.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 23:2023.10.04.560843. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.04.560843. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2024 Sep 06;12:RP91605. doi: 10.7554/eLife.91605. PMID: 38562725 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Adamek M. VERA - A versatile electrode localization framework. Version 1.0.0Zenodo. 2022 doi: 10.5281/zenodo.7486842. - DOI
-
- Beck AM, He M, Gutierrez R, Purdon PL. An Iterative Search Algorithm to Identify Oscillatory Dynamics in Neurophysiological Time Series. bioRxiv. 2022 doi: 10.1101/2022.10.30.514422. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

