Real-world treatment patterns and outcomes in patients with HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer treated with chemotherapy in the United States
- PMID: 39241499
- PMCID: PMC11406087
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.103691
Real-world treatment patterns and outcomes in patients with HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer treated with chemotherapy in the United States
Abstract
Background: Until recently, treatment options for patients with hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor 2-negative (HR+/HER2-) metastatic breast cancer (mBC) and resistance to endocrine therapy were limited to chemotherapy. This real-world study describes treatment patterns and outcomes in patients treated with chemotherapy in the United States before approval of antibody-drug conjugates.
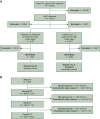
Patients and methods: This retrospective, observational study included adults with HR+/HER2- mBC from the ConcertAI Patient360™ Breast Cancer dataset who initiated their first chemotherapy in the metastatic setting between January 2011 and June 2021. Treatment patterns were described; real-world overall survival, time to next treatment or death, and real-world progression-free survival were evaluated for all eligible patients and patients treated with subsequent chemotherapy. Index dates were the start date of each chemotherapy treatment.
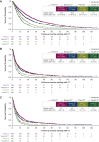
Results: Among 1545 eligible patients, 76% were white, 12% had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status ≥2, 38% had de novo mBC, and median age was 61 years (range, 52-69 years). Within the index period, capecitabine was used the most as the first chemotherapy agent and decreased in later treatments, while the use of eribulin increased between first and fourth chemotherapies. Median (95% confidence interval) real-world overall survival was 23.3 months (21.3-25.4 months) from start of first chemotherapy, time to next treatment or death was 6.5 months (5.9-7.1 months), and real-world progression-free survival was 6.9 months (6.4-7.6 months); median times from second, third, and fourth chemotherapies decreased with each additional chemotherapy treatment.
Conclusions: This real-world study demonstrates that for patients with HR+/HER2- mBC, chemotherapy provides relatively limited survival benefit which decreases with each additional chemotherapy line, and highlights the need for improved treatment options.
Keywords: HER2-negative; RWE; antibody–drug conjugates; chemotherapy; hormone receptor-positive; metastatic breast cancer.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Wolff A.C., Somerfield M.R., Dowsett M., et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: ASCO-College of American Pathologists Guideline Update. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41(22) - PubMed
-
- National Cancer Institute Cancer stat facts: female breast cancer subtypes. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast-subtypes.html Available at.
-
- Gennari A., Andre F., Barrios C.H., et al. ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for the diagnosis, staging and treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2021;32(12):1475–1495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

