The circadian clock in enamel development
- PMID: 39242565
- PMCID: PMC11379899
- DOI: 10.1038/s41368-024-00317-9
The circadian clock in enamel development
Abstract
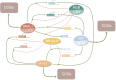
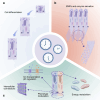
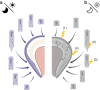
Circadian rhythms are self-sustaining oscillations within biological systems that play key roles in a diverse multitude of physiological processes. The circadian clock mechanisms in brain and peripheral tissues can oscillate independently or be synchronized/disrupted by external stimuli. Dental enamel is a type of mineralized tissue that forms the exterior surface of the tooth crown. Incremental Retzius lines are readily observable microstructures of mature tooth enamel that indicate the regulation of amelogenesis by circadian rhythms. Teeth enamel is formed by enamel-forming cells known as ameloblasts, which are regulated and orchestrated by the circadian clock during amelogenesis. This review will first examine the key roles of the circadian clock in regulating ameloblasts and amelogenesis. Several physiological processes are involved, including gene expression, cell morphology, metabolic changes, matrix deposition, ion transportation, and mineralization. Next, the potential detrimental effects of circadian rhythm disruption on enamel formation are discussed. Circadian rhythm disruption can directly lead to Enamel Hypoplasia, which might also be a potential causative mechanism of amelogenesis imperfecta. Finally, future research trajectory in this field is extrapolated. It is hoped that this review will inspire more intensive research efforts and provide relevant cues in formulating novel therapeutic strategies for preventing tooth enamel developmental abnormalities.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

