A probiotic Limosilactobacillus fermentum GR-3 mitigates colitis-associated tumorigenesis in mice via modulating gut microbiome
- PMID: 39242568
- PMCID: PMC11379937
- DOI: 10.1038/s41538-024-00307-5
A probiotic Limosilactobacillus fermentum GR-3 mitigates colitis-associated tumorigenesis in mice via modulating gut microbiome
Abstract
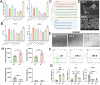
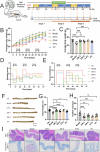
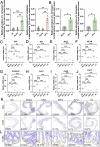
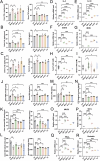
Bacterial therapy for colorectal cancer (CRC) represents a burgeoning frontier. The probiotic Limosilactobacillus fermentum GR-3, derived from traditional food "Jiangshui", exhibited superior antioxidant capacity by producing indole derivatives ICA and IPA. In an AOM/DSS-induced CRC mouse model, GR-3 treatment alleviated weight loss, colon shortening, rectal bleeding and intestinal barrier disruption by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. GR-3 colonization in distant colon induced apoptosis and reduced tumor incidence by 51.2%, outperforming the control strain and vitamin C. The beneficial effect of GR-3 on CRC was associated with gut microbiome modulation, increasing SCFA producer Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group and suppressing pro-inflammatory strain Bacteroides. Metagenomic and metabolic analyses revealed that GR-3 intervention upregulated antioxidant genes (xseA, ALDH) and butyrate synthesis gene (bcd), while increasing beneficial metabolites (SCFAs, ICA, IPA, VB12 and VD3) and reducing harmful secondary bile acids. Overall, GR-3 emerges as a promising candidate in CRC therapy, offering effective gut microbiome remediation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Patel, S. G., Karlitz, J. J., Yen, T., Lieu, C. H. & Boland, C. R. The rising tide of early-onset colorectal cancer: a comprehensive review of epidemiology, clinical features, biology, risk factors, prevention, and early detection. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol.7, 262–274 (2022). 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00426-X - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

