Index of Consciousness monitoring may effectively predict and prevent circulatory stress induced by endotracheal intubation under general anesthesia: a prospective randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 39243003
- PMCID: PMC11378600
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-024-02701-8
Index of Consciousness monitoring may effectively predict and prevent circulatory stress induced by endotracheal intubation under general anesthesia: a prospective randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: The primary objective of anesthesiologists during the induction of anaesthesia is to mitigate the operative stress response resulting from endotracheal intubation. In this prospective, randomized controlled trial, our aim was to assess the feasibility and efficacy of employing Index of Consciousness (IoC, IoC1 and IoC2) monitoring in predicting and mitigating circulatory stress induced by endotracheal intubation for laparoscopic cholecystectomy patients under general anesthesia (GA).
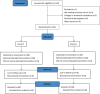
Methods: We enrolled one hundred and twenty patients scheduled for laparoscopic cholecystectomy under GA and randomly allocated them to two groups: IoC monitoring guidance (Group T, n = 60) and bispectral index (BIS) monitoring guidance (Group C, n = 60). The primary endpoints included the heart rate (HR) and mean arterial pressure (MAP) of the patients, as well as the rate of change (ROC) at specific time points during the endotracheal intubation period. Secondary outcomes encompassed the systemic vascular resistance index (SVRI), cardiac output index (CI), stroke volume index (SVI), ROC at specific time points, the incidence of adverse events (AEs), and the induction dosage of remifentanil and propofol during the endotracheal intubation period in both groups.
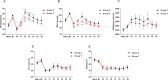
Results: The mean (SD) HR at 1 min after intubation under IoC monitoring guidance was significantly lower than that under BIS monitoring guidance (76 (16) beats/min vs. 82 (16) beats/min, P = 0.049, respectively). Similarly, the mean (SD) MAP at 1 min after intubation under IoC monitoring guidance was lower than that under BIS monitoring guidance (90 (20) mmHg vs. 98 (19) mmHg, P = 0.031, respectively). At each time point from 1 to 5 min after intubation, the number of cases with HR ROC of less than 10% in Group T was significantly higher than in Group C (P < 0.05). Furthermore, between 1 and 3 min and at 5 min post-intubation, the number of cases with HR ROC between 20 to 30% or 40% in Group T was significantly lower than that in Group C (P < 0.05). At 1 min post-intubation, the number of cases with MAP ROC of less than 10% in Group T was significantly higher than that in Group C (P < 0.05), and the number of cases with MAP ROC between 10 to 20% in Group T was significantly lower than that in Group C (P < 0.01). Patients in Group T exhibited superior hemodynamic stability during the peri-endotracheal intubation period compared to those in Group C. There were no significant differences in the frequencies of AEs between the two groups (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: This promising monitoring technique has the potential to predict the circulatory stress response, thereby reducing the incidence of adverse reactions during the peri-endotracheal intubation period. This technology holds promise for optimizing anesthesia management.
Trail registration: Chinese Clinical Trail Registry Identifier: ChiCTR2300070237 (20/04/2022).
Keywords: Bispectral index; Endotracheal intubation; Index of Consciousness; Stress response.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wang B, Peng G, Chen L, Guo M, Zhou J, Liu Y, Chen Z, Wang L. Effect of transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation on remifentanil dosage during craniotomy aneurysm clipping: a prospective, randomized controlled study. BMC complementary medicine and therapies. 2023;23(1):453. 10.1186/s12906-023-04297-x. 10.1186/s12906-023-04297-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gupta M, Rohilla R, Gupta P, Tamilchelvan H, Joshi U, Kanwat J. Nebulized dexmedetomidine for attenuating hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation in adult patients undergoing surgeries under general anaesthesia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023;23(1):406. 10.1186/s12871-023-02366-9. 10.1186/s12871-023-02366-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feng S, Yang S, Xiao W, Wang X, Yang K, Wang T. Effects of perioperative goal-directed fluid therapy combined with the application of alpha-1 adrenergic agonists on postoperative outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018;18(1):113. 10.1186/s12871-018-0564-y. 10.1186/s12871-018-0564-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

