Sodium Houttuyniae attenuates ferroptosis by regulating TRAF6-c-Myc signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury (ALI)
- PMID: 39243105
- PMCID: PMC11380410
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-024-00787-x
Sodium Houttuyniae attenuates ferroptosis by regulating TRAF6-c-Myc signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury (ALI)
Abstract
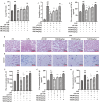
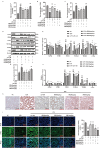
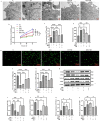
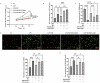
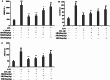
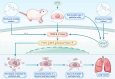
The impact of Sodium Houttuyniae (SH) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI has been investigated extensively. However, it remains ambiguous whether ferroptosis participates in this process. This study aimed to find out the impacts and probable mechanisms of SH on LPS-induced ferroptosis. A rat ALI model and type II alveolar epithelial (ATII) cell injury model were treated with LPS. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining, and Giemsa staining were executed to ascertain the effects of SH on LPS-induced ALI. Moreover, Transmission electron microscopy, Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8), ferrous iron colorimetric assay kit, Immunohistochemistry, Immunofluorescence, Reactive oxygen species assay kit, western blotting (Wb), and qRT-PCR examined the impacts of SH on LPS-induced ferroptosis and ferroptosis-related pathways. Theresults found that by using SH treatment, there was a remarkable attenuation of ALI by suppressing LPS-induced ferroptosis. Ferroptosis was demonstrated by a decline in the levels of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), FTH1, and glutathione (GSH) and a surge in the accumulation of malondialdehyde (MDA), reactive oxygen species (ROS), NOX1, NCOA4, and Fe2+, and disruption of mitochondrial structure, which were reversed by SH treatment. SH suppressed ferroptosis by regulating TRAF6-c-Myc in ALI rats and rat ATII cells. The results suggested that SH treatment attenuated LPS-induced ALI by repressing ferroptosis, and the mode of action can be linked to regulating the TRAF6-c-Myc signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Ferroptosis; Sodium Houttuyniae; TRAF6-c-Myc pathway.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isoginkgetin inhibits macrophage activation and ferroptosis of lung epithelial cells under lipopolysaccharide-induced immunological stress via HOXA5-dependent inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κΒ signaling pathway.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2025 Sep;502:117413. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2025.117413. Epub 2025 May 25. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40425070
-
Biyuan Tongqiao Granules ameliorates acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharides by PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Aug 29;352:120232. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120232. Epub 2025 Jul 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40609811
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-secreted KGF ameliorates acute lung injury via the Gab1/ERK/NF-κB signaling axis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jul 10;30(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00757-z. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40640718 Free PMC article.
-
Brazilin alleviates acute lung injury via inhibition of ferroptosis through the SIRT3/GPX4 pathway.Apoptosis. 2025 Apr;30(3-4):768-783. doi: 10.1007/s10495-024-02058-w. Epub 2024 Dec 25. Apoptosis. 2025. PMID: 39720978
-
Targeting ferroptosis using Chinese herbal compounds to treat respiratory diseases.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jul 25;130:155738. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155738. Epub 2024 Jun 1. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38824825
References
-
- Yang JX, Li M, Chen XO, Lian QQ, Wang Q, Gao F, Jin SW, Zheng SX. Lipoxin A(4) ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury through stimulating epithelial proliferation, reducing epithelial cell apoptosis and inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Respir Res. 2019;20:192. 10.1186/s12931-019-1158-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

