Genetic diversity analysis and DNA fingerprint construction of Zanthoxylum species based on SSR and iPBS markers
- PMID: 39244564
- PMCID: PMC11380355
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-024-05373-1
Genetic diversity analysis and DNA fingerprint construction of Zanthoxylum species based on SSR and iPBS markers
Abstract
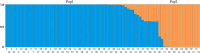
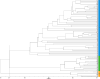
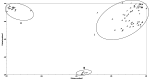
Zanthoxylum is a versatile economic tree species utilized for its spice, seasoning, oil, medicinal, and industrial raw material applications, and it has a lengthy history of cultivation and domestication in China. This has led to the development of numerous cultivars. However, the phenomenon of mixed cultivars and confusing names has significantly obstructed the effective utilization of Zanthoxylum resources and industrial development. Consequently, conducting genetic diversity studies and cultivar identification on Zanthoxylum are crucial. This research analyzed the genetic traits of 80 Zanthoxylum cultivars using simple sequence repeat (SSR) and inter-Primer Binding Site (iPBS) molecular markers, leading to the creation of a DNA fingerprint. This study identified 206 and 127 alleles with 32 SSR markers and 10 iPBS markers, respectively, yielding an average of 6.4 and 12.7 alleles (Na) per marker. The average polymorphism information content (PIC) for the SSR and iPBS markers was 0.710 and 0.281, respectively. The genetic similarity coefficients for the 80 Zanthoxylum accessions ranged from 0.0947 to 0.9868 and from 0.2206 to 1.0000, with mean values of 0.3864 and 0.5215, respectively, indicating substantial genetic diversity. Cluster analysis, corroborated by principal coordinate analysis (PCoA), categorized these accessions into three primary groups. Analysis of the genetic differentiation among the three Zanthoxylum (Z. bungeanum, Z. armatum, and Z. piperitum) populations using SSR markers revealed a mean genetic differentiation coefficient (Fst) of 0.335 and a gene flow (Nm) of 0.629, suggesting significant genetic divergence among the populations. Molecular variance analysis (AMOVA) indicated that 65% of the genetic variation occurred within individuals, while 35% occurred among populations. Bayesian model-based analysis of population genetic structure divided all materials into two groups. The combined PI and PIsibs value of the 32 SSR markers were 4.265 × 10- 27 and 1.282 × 10- 11, respectively, showing strong fingerprinting power. DNA fingerprints of the 80 cultivars were established using eight pairs of SSR primers, each assigned a unique numerical code. In summary, while both markers were effective at assessing the genetic diversity and relationships of Zanthoxylum species, SSR markers demonstrated superior polymorphism and cultivar discrimination compared to iPBS markers. These findings offer a scientific foundation for the conservation and sustainable use of Zanthoxylum species.
Keywords: Zanthoxylum; DNA fingerprint; Genetic diversity; Genetic structure; SSR markers; iPBS markers.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Feng S, Yang T, Liu Z, et al. Genetic diversity and relationships of wild and cultivated Zanthoxylum germplasms based on sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol. 2015;62:1193–204. 10.1007/s10722-015-0222-x - DOI
-
- Feng S, Liu Z, Chen L, et al. Phylogenetic relationships among cultivated Zanthoxylum species in China based on cpDNA markers. Tree Genet Genomes. 2016;12:1–9. 10.1007/s11295-016-1005-z - DOI
-
- Xie DY, Chen QY. Utilization of Chinese prickly ash in ancient Chinese people’s Diet. Chuxiong Normal Univ. 2013;28:10–3.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2019YFD1001200/National Key R&D Program of China
- 2019YFD1001200/National Key R&D Program of China
- 2019YFD1001200/National Key R&D Program of China
- 2019YFD1001200/National Key R&D Program of China
- 2019YFD1001200/National Key R&D Program of China
- 2021YFYZ0032/Research on the Selection and Breeding of New High-Quality and Labor-Saving Cultivars of Chinese Pepper and Supporting Technology
- 2021YFYZ0032/Research on the Selection and Breeding of New High-Quality and Labor-Saving Cultivars of Chinese Pepper and Supporting Technology
- 2021YFYZ0032/Research on the Selection and Breeding of New High-Quality and Labor-Saving Cultivars of Chinese Pepper and Supporting Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

