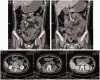
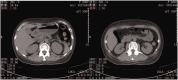
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia with pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a case report
- PMID: 39246070
- PMCID: PMC11382223
- DOI: 10.1177/03000605241274581
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia with pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a case report
Abstract
Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis (PCI) is a rare condition characterized by air accumulation within the subserosa or submucosa of the gastrointestinal wall. We herein report a case involving a woman in her early 30s who developed PCI after undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. The patient had a history of multiple COVID-19 infections. Imaging revealed extensive pneumoperitoneum and mesenteric emphysema; nevertheless, the patient remained clinically stable with a benign abdominal examination. She eventually recovered after 1 month of conservative treatment. We believe the PCI in this case had a multifactorial etiology, potentially involving both HSCT and COVID-19. Raising awareness of PCI may help avoid unnecessary surgical interventions and associated morbidity.
Keywords: COVID-19; Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis; acute lymphoblastic leukemia; graft-versus-host disease; immunosuppression; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lee KS, Hwang S, Hurtado RS, et al.. Distinguishing benign and life-threatening pneumatosis intestinalis in patients with cancer by CT imaging features. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2013; 200: 1042–1047. - PubMed
-
- Ma W, Zhang C, Sun MW, et al.. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis: a case report and literature review. Asian J Surg 2023; 46: 2581–2582. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous