Complement C5a Receptor Signaling in Macrophages Enhances Trained Immunity Through mTOR Pathway Activation
- PMID: 39246622
- PMCID: PMC11377950
- DOI: 10.4110/in.2024.24.e24
Complement C5a Receptor Signaling in Macrophages Enhances Trained Immunity Through mTOR Pathway Activation
Abstract
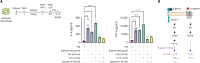
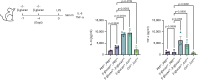
Complement C5a receptor (C5aR) signaling in immune cells has various functions, inducing inflammatory or anti-inflammatory responses based on the type of ligand present. The Co1 peptide (SFHQLPARSRPLP) has been reported to activate C5aR signaling in dendritic cells. We investigated the effect of C5aR signaling via the Co1 peptide on macrophages. In peritoneal macrophages, the interaction between C5aR and the Co1 peptide activated the mTOR pathway, resulting in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Considering the close associations of mTOR signaling with IL-6 and TNF-α in macrophage training, our findings indicate that the Co1 peptide amplifies β-glucan-induced trained immunity. Overall, this research highlights a previously underappreciated aspect of C5aR signaling in trained immunity, and posits that the Co1 peptide is a potentially effective immunomodulator for enhancing trained immunity.
Keywords: Adjuvants, immunogenic; C5a receptor; Immunomodulator; Inflammation; Trained immunity.
Copyright © 2024. The Korean Association of Immunologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Walport MJ. Complement. First of two parts. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1058–1066. - PubMed
-
- Pandey S, Maharana J, Li XX, Woodruff TM, Shukla AK. Emerging insights into the structure and function of complement C5a receptors. Trends Biochem Sci. 2020;45:693–705. - PubMed
-
- Mastellos DC, Hajishengallis G, Lambris JD. A guide to complement biology, pathology and therapeutic opportunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2024;24:118–141. - PubMed
-
- Seow V, Lim J, Iyer A, Suen JY, Ariffin JK, Hohenhaus DM, Sweet MJ, Fairlie DP. Inflammatory responses induced by lipopolysaccharide are amplified in primary human monocytes but suppressed in macrophages by complement protein C5a. J Immunol. 2013;191:4308–4316. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

