Factors Contributing to the Development of Neuropsychiatric Manifestations in Persons With Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39246867
- PMCID: PMC11380372
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.66432
Factors Contributing to the Development of Neuropsychiatric Manifestations in Persons With Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is the most common chronic demyelinating disease affecting the central nervous system (CNS) and is distinguished by neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. It has four categories based on clinical course, with relapsing-remitting being the most common type. MS predominantly manifests with motor and sensory dysfunctions. However, neuropsychiatric manifestations such as depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder are not uncommon. Various factors may contribute to the development of these manifestations; therefore, this study aimed to unravel them. This systematic review implemented the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines. Five databases (PubMed, PubMed Central (PMC), ScienceDirect, Cochrane Library, and Google Scholar) were used to acquire articles published in the past five years. After screening and quality appraisal were completed, eight articles were deemed eligible for inclusion in this study. The study designs included cohort, cross-sectional, randomized-controlled trial (RCT), case report, case-control, and narrative review. The development of neuropsychiatric manifestations in persons with MS is influenced by various factors. These were categorized into morphological changes of the brain, immunological mechanisms, socioeconomic factors, and individual factors for discussion. Each factor was found to intermingle with the others, requiring further research to understand the features that each factor contributes. This is crucial for improving the quality of life (QOL) and prognosis for persons living with MS.
Keywords: anxiety; cognitive impairment; depression; mental health; mood disorder; multiple sclerosis; neurodegeneration; neuropsychiatric symptoms; quality of life; risk factors.
Copyright © 2024, Sangster et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
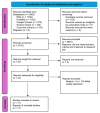
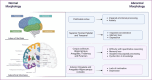
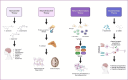
References
-
- Anxiety and depression as comorbidities of multiple sclerosis. Mustač F, Pašić H, Medić F, et al. https://www.psychiatria-danubina.com/UserDocsImages/pdf/dnb_vol33_noSupp.... Psychiatr Danub. 2021;33:480–485. - PubMed
-
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms of multiple sclerosis. Tampi RR, Tampi DJ, Pittinger L. https://www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/neuropsychiatric-symptoms-multiple... Psychiatr Times. 2021;38:24–27.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
