Advancing Research on Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Inhibitors: A Scientometric Analysis
- PMID: 39247108
- PMCID: PMC11377008
- DOI: 10.21315/mjms2024.31.4.2
Advancing Research on Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Inhibitors: A Scientometric Analysis
Abstract
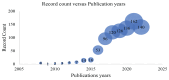
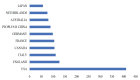
Atherosclerosis is characterised by the accumulation of fatty deposits and plaque as a result of a continuously high level of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in the blood. The primary objective of this research is to assess the current status of knowledge, research endeavours and developmental trajectories about proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors in correlation with atherosclerosis treatment. Additionally, this study aims to compile bibliometric and scientometric investigations within this domain through rigorous scientometric analysis. Analysing the bibliometric landscape and global research trends associated with PCSK9 inhibitors can contribute valuable insights into comprehending atherosclerosis. This is exemplified by examining publications within the Web of Science Core Collection (WOSCC) database from 2008 to 2022. Citespace was used for frequency, co-occurrence, co-citation, grouping and burst analysis, and Microsoft Excel was used to manage descriptive datasets. Eight hundred eighty-five publications available from WOSCC database between the years 2008 and 2022 were extracted and examined. Over the period, 3,138 collaborating institutions from 87 countries, a staggering 7,750 writers involved and 325 distinct journals published about PCSK9 inhibitors studies. Among authors, Sabatine et al. and the journal The New England Journal of Medicine has had the most significant impact. Lipid-lowering therapy and bempedoic acid are the most prominent topical clusters associated with PCSK9 inhibitors, and the most often used keywords are efficacy, safety and PCSK9 inhibitors. We believe this is the first comprehensive analysis of PCSK9 inhibitors research and publications conducted using Scientometric. These results demonstrate the nascence of PCSK9 inhibitors research. They may encourage a wide range of stakeholders, particularly early career researchers from various disciplines, to work together in the future.
Keywords: PCSK9; PCSK9 inhibitors; atherosclerosis; bempedoic acid; lipid-lowering therapy.
© Penerbit Universiti Sains Malaysia, 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None.
Figures





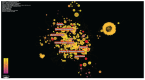
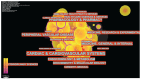
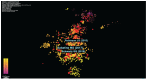


References
-
- Amput P, McSweeney C, Palee S, Phrommintikul A, Chattipakorn SC, Chattipakorn N. The effects of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors on lipid metabolism and cardiovascular function. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109(October 2018):1171–1180. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.138. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Satyanarayana, Chakrapani . Biochemistry. 4th ed. A division of Reed Elsevier India Private Limited: Elsevier; 2013.
-
- Mohamad H, Razak MFA, Kamaruddin NN, Din LHM, Asari A, Andriani Y, et al. PCSK9 inhibitory activity of marine-derived compounds, aaptaminoids, and benzamide originated from Aaptos aaptos and Acanthaster planci as a potential treatment for atherosclerosis. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2020;10(8):111–123. doi: 10.7324/JAPS.2020.10813. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
