Efficacy and Safety of General Anesthesia Induction with Ciprofol in Hip Fracture Surgery of Elderly Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 39247794
- PMCID: PMC11380857
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S475176
Efficacy and Safety of General Anesthesia Induction with Ciprofol in Hip Fracture Surgery of Elderly Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Ciprofol is a new intravenous sedative / anesthetic drug. In recent years, many clinical studies have also confirmed the sedative effect of ciprofol. However, more clinical research is still needed on its clinical application characteristics in special populations.
Objective: The aim of this study was to compare the clinical effects of ciprofol and propofol in general anesthesia induction of elderly patients.
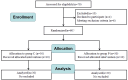
Methods: 60 elderly (aged ≥ 75 years) patients underwent hip fracture surgery were randomly into two groups of a 1:1 ratio. Group C (ciprofol group): 0.3mg/kg ciprofol was infused. Group P (propofol group): 1.5mg/kg propofol was infused. The observation period was from the infusion of test drug to 5 min after endotracheal intubation. The primary outcomes included the incidence of severe hypotension and hypotension during the observation period. The secondary outcomes were as follows: the success rate of general anesthesia induction, the number of additional sedation, the time of loss of consciousness (LOC), Δ MAP, Δ HR, adverse events and the frequency of vasoactive drugs used.
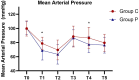
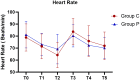
Results: Finally, 60 subjects completed the study. Compared with Group P, the incidence of severe hypotension in Group C was lower (26.7% vs 53.3%, P = 0.035), the incidence of hypotension was also lower (36.7% vs 63.3%, P = 0.037), Δ MAP in Group C was significantly lower (31.4 ± 11.4 vs 39.6 ± 15.7, P = 0.025), the frequency of ephedrine used and the incidence of injection pain in Group C were also significantly lower.
Conclusion: Ciprofol showed similar efficacy to propofol when used for general anesthesia induction in elderly patients underwent hip fracture surgery and could maintain more stable blood pressure.
Keywords: Ciprofol; Hip fracture surgery; elderly; general anesthesia; hypotension.
© 2024 Lu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Meuret P, Bouvet L, Villet B, et al. hypobaric unilateral spinal anaesthesia versus general anaesthesia in elderly patients undergoing hip fracture surgical repair: A prospective randomised open trial. Turk. J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2018;46(2):121–130. doi: 10.5152/TJAR.2018.90699 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

