Zongertinib (BI 1810631), an Irreversible HER2 TKI, Spares EGFR Signaling and Improves Therapeutic Response in Preclinical Models and Patients with HER2-Driven Cancers
- PMID: 39248702
- PMCID: PMC11726021
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-0306
Zongertinib (BI 1810631), an Irreversible HER2 TKI, Spares EGFR Signaling and Improves Therapeutic Response in Preclinical Models and Patients with HER2-Driven Cancers
Abstract
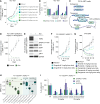
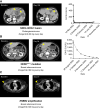
Mutations in ERBB2 (encoding HER2) occur in 2% to 4% of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and confer poor prognosis. ERBB-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitors, approved for treating other HER2-dependent cancers, are ineffective in HER2-mutant NSCLC due to dose-limiting toxicities or suboptimal potency. We report the discovery of zongertinib (BI 1810631), a covalent HER2 inhibitor. Zongertinib potently and selectively blocks HER2, while sparing EGFR, and inhibits the growth of cells dependent on HER2 oncogenic driver events, including HER2-dependent human cancer cells resistant to trastuzumab deruxtecan. Zongertinib displays potent antitumor activity in HER2-dependent human NSCLC xenograft models and enhances the activities of antibody-drug conjugates and KRASG12C inhibitors without causing obvious toxicities. The preclinical efficacy of zongertinib translates in objective responses in patients with HER2-dependent tumors, including cholangiocarcinoma (SDC4-NRG1 fusion) and breast cancer (V777L HER2 mutation), thus supporting the ongoing clinical development of zongertinib. Significance: HER2-mutant NSCLC poses a challenge in the clinic due to limited options for targeted therapies. Pan-ERBB blockers are limited by wild-type EGFR-mediated toxicity. Zongertinib is a highly potent and wild-type EGFR-sparing HER2 inhibitor that is active in HER2-driven tumors in the preclinical and clinical settings.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
B. Wilding reports grants from the Austrian Promotion Agency during the conduct of the study; in addition, B. Wilding has a patent for WO2021/213800 pending and is a full-time employee of Boehringer Ingelheim. L. Woelflingseder reports grants from the Austrian Research Promotion Agency during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim RCV outside the submitted work and is a full-time employee of Boehringer Ingelheim RCV. A. Baum reports grants from the Austrian Research Promotion Agency FFG grants during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim RCV outside the submitted work and is a full-time employee of Boehringer Ingelheim RCV. K. Chylinski reports grants from the Austrian Research Promotion Agency during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim RCV outside the submitted work. G. Vainorius reports grants from the Austrian Research Promotion Agency during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim RCV outside the submitted work and is a full-time employee of Boehringer Ingelheim RCV. N. Gibson reports other support from Boehringer Ingelheim & Co. KG outside the submitted work; in addition, N. Gibson has a patent for WO2024133325A1 pending. I.C. Waizenegger reports grants from the Austrian Research Promotion Agency during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim RCV GmbH & Co. KG outside the submitted work and is a full-time employee of Boehringer Ingelheim RCV GmbH & Co. KG. D. Gerlach reports grants from the Austrian Research Promotion Agency FFG during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim RCV outside the submitted work and is a full-time employee of Boehringer Ingelheim RCV. M. Augsten reports grants from the Austrian Research Promotion Agency during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim RCV GmbH Co. KG outside the submitted work and is a full-time employee of Boehringer Ingelheim RCV GmbH Co. KG. S. Tilandyova reports grants from the Austrian Research Promotion Agency during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim RCV outside the submitted work and is a full-time employee of Boehringer Ingelheim RCV. D. Scharn reports grants from the Austrian Research Promotion Agency during the conduct of the study; in addition, D. Scharn has a patent 20210332054 issued to Assignee: Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH (Ingelheim am Rhein), a patent 20230374021 pending, and a patent 11608343 issued to Assignee: Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH (Ingelheim am Rhein) and reports being a former employee of Boehringer Ingelheim. M.A. Pearson reports other support from Boehringer Ingelheim during the conduct of the study and outside the submitted work. J. Popow reports personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim during the conduct of the study. A.C. Obenauf reports grants from Boehringer Ingelheim during the conduct of the study. N. Yamamoto reports grants from Boehringer Ingelheim during the conduct of the study and grants from Astellas, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Eisai, Taiho, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Novartis, Eli Lilly, AbbVie, Daiichi Sankyo, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Kyowa Kirin, Takeda, Ono Pharmaceutical, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, MSD, Merck, GSK, Sumitomo Pharma, Chiome Bioscience, Otsuka, Carna Biosciences, Genmab, Shionogi, Toray, KAKEN, AstraZeneca, InventisBio, Rakuten Medical, Amgen, and Bicycle Therapeutics and personal fees from Eisai, Takeda, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cmic, personal fees from Chugai Pharmaceutical, Merck, Healios, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Rakuten Medical, Noile-Immune Biotech, and Daiichi Sankyo outside the submitted work. F.L. Opdam reports other support from Boehringer Ingelheim during the conduct of the study and is a principal investigator of studies with Astra zeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Crescendo, Cytovation, GSK, Incyte, Lilly, Merus, Pierre Fabre, Relay, RevMed, Roche, and Taiho, with institutional provision of intellectual property. S. Kohsaka reports grants from Boehringer Ingelheim during the conduct of the study and grants from Chordia Therapeutics, Eisai, Konica Minolta, CIMIC, and H.U. Group Research Institute. Group Research Institute outside the submitted work. N. Kraut reports grants from the Austrian Research Promotion Agency FFG during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim RCV outside the submitted work and is a full-time employee of Boehringer Ingelheim RCV. J.V. Heymach reports personal fees from AbbVie, AnHeart Therapeutics, BioCurity Pharmaceuticals, BioNTech, , DAVA Oncology, Eli Lilly, EMD Serono, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, , Moffitt Cancer Center, ModeX, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, OncoCyte, and Sanofi and personal fees and other support from Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Takeda, Mirati Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, and AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. F. Solca reports grants from the Austrian Research Promotion Agency during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim RCV outside the submitted work and is a full-time employee of Boehringer Ingelheim RCV. R.A. Neumüller reports grants from the Austrian Research Promotion Agency (grant numbers 865390, 872827, and 879012) during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim RCV outside the submitted work; in addition, R.A. Neumüller has a patent for WO2021/213800 pending. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures




References
-
- Wang Z. ErbB receptors and cancer. Methods Mol Biol 2017;1652:3–35. - PubMed
-
- Hynes NE, MacDonald G. ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2009;21:177–84. - PubMed
-
- Citri A, Yarden Y. EGF–ERBB signalling: towards the systems level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006;7:505–16. - PubMed
-
- Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Procter M, Leyland-Jones B, Goldhirsch A, Untch M, Smith I, et al. Trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2005;353:1659–72. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

