Safety and Effectiveness of Concomitant iGlarLixi and SGLT-2i Use in People with T2D During Ramadan Fasting: A SoliRam Study Sub-analysis
- PMID: 39249672
- PMCID: PMC11467161
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-024-01642-2
Safety and Effectiveness of Concomitant iGlarLixi and SGLT-2i Use in People with T2D During Ramadan Fasting: A SoliRam Study Sub-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of this work was to assess the safety and effectiveness of concomitant iGlarLixi and sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i) use in adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D) who fasted during Ramadan.
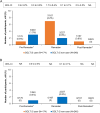
Methods: Of the 420 eligible participants from the SoliRam study, 174 were using SGLT-2i in addition to iGlarLixi and 246 were not using SGLT-2i, referred to as SGLT-2i user and non-user, respectively. The primary endpoint was the proportion of participants experiencing ≥ 1 severe and/or symptomatic documented (< 70 mg/dl [< 3.9 mmol/l]) hypoglycemia.
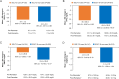
Results: More than 50% of participants in both groups were male. The mean weight, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) were similar in both groups. Approximately half of participants in the SGLT-2i-user group and ~ 25% participants in the SGLT-2i-non-user group were on two oral anti-hyperglycemic drugs (OADs), whereas ~ 20% in the SGLT-2i-user group and ~ 1% of participants in the SGLT-2i-non-user group were on three OADs in addition to iGlarLixi. Around 35% and 55% of participants in the SGLT-2i-user and SGLT-2i-non-user groups, respectively, were taking concurrent sulphonylureas. About 97% of participants in both groups were able to fast for ≥ 25 days. The incidence of primary endpoint was low in both groups; SGLT-2i user: 0.6%, 4.2%, and 0.6% and SGLT-2i-non-user: 1.3%, 0.9% and 0% during pre-Ramadan, Ramadan, and post-Ramadan period, respectively. The incidence of severe and/or symptomatic documented (< 54 mg/dl [< 3.0 mmol/l]) hypoglycemia events was also low throughout the study, including during Ramadan. No severe hypoglycemia occurred during Ramadan in either group. Improvements in HbA1c and FPG, with a small reduction in weight, were observed from pre- to post-Ramadan in both groups. No serious adverse event was reported in either group.
Conclusions: Concomitant iGlarLixi and SGLT-2i therapy with or without other OADs was demonstrated to be safe in adults with T2D during Ramadan fast, with a low risk of hypoglycemia and improvements in glycemic outcomes.
Keywords: Fasting; Hypoglycemia; Ramadan; SGLT-2i; Type 2 diabetes; iGlarLixi.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Mohamed Hassanein is an advisory board member for Sanofi, Boehringer Ingelheim and Novo Nordisk and a speaker for Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, LifeScan, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi and has received lecturer/other fees from Sanofi, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly and Company, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Janssen and LifeScan. Rachid Malek has received speaker fees and advisory board honoraria from Novo Nordisk. Saud Al Sifri has acted as an adviser and speaker for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly and Company, MSD, Novartis, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi. Rakesh Kumar Sahay is an advisory board member for Boehringer Ingelheim, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Eli Lilly and Company and Sanofi and a speaker for Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi. Mehmet Akif Buyukbese has received speaker fees from Eli Lilly and Company and speaker/other fees from Novartis and Sanofi. Khier Djaballah is an employee of Sanofi and may hold shares/stocks in the company. Lydie Melas-Melt is an employee of IVIDATA Life Sciences. Inass Shaltout is a speaker and advisory board member for Sanofi, Novartis, MSD, AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly and Company, Servier and Abbott.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

