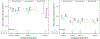Markers of Maternal Bone and Renal Toxicity Through 50 Weeks Postpartum: IMPAACT 2010 (VESTED) Trial
- PMID: 39250651
- PMCID: PMC11384307
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000003478
Markers of Maternal Bone and Renal Toxicity Through 50 Weeks Postpartum: IMPAACT 2010 (VESTED) Trial
Abstract
Background: Safety data from randomized trials of antiretrovirals in pregnancy are scarce. We evaluated maternal bone and renal data from the International Maternal Pediatric Adolescent AIDS Clinical Trials Network 2010 trial, which compared the safety and efficacy of 3 antiretroviral therapy regimens started in pregnancy: dolutegravir + emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (DTG + FTC/TAF), dolutegravir + emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (DTG + FTC/TDF), and efavirenz/emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (EFV/FTC/TDF).
Methods: A subset of participants underwent dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scans at postpartum week 50 only. Maternal bone mineral density (BMD) Z-scores were compared between arms. Maternal creatinine was measured at enrolment and periodically through week 50 postpartum, and by-arm differences in average weekly change in estimated creatinine clearance were compared.
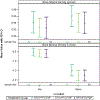
Results: Six hundred forty-three participants were randomized to DTG + FTC/TAF (N = 217) or DTG + FTC/TDF (N = 215) or EFV/FTC/TDF (N = 211). Median age = 27 years (IQR 23, 32), median CD4 count = 466 cells/mm3 (IQR 308, 624); 564 (88%) women enrolled in Africa and 479 (74%) breastfed. Week 50 postpartum dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry results from 154 women were included in the analysis. Hip and spine BMD was on average higher in women in the DTG + FTC/TAF and lower in the DTG + FTC/TDF and EFV/FTC/TDF arms, but no significant differences in BMD Z-scores were observed between treatment groups. The weekly rate of change in estimated creatinine clearance differed among treatment groups during the antepartum period, but not over the full study follow-up.
Conclusions: Markers of bone and renal toxicity did not differ significantly through week 50 postpartum among women randomized to start DTG + FTC/TAF or DTG + FTC/TDF or EFV/FTC/TDF in pregnancy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03048422.
Copyright © 2024 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Prevention of mother-to-child transmission: estimates by WHO region. World Health Organization; 2023. Updated 7 Jul 2023. https://apps.who.int/gho/data/view.main.23500REG?lang=en.
-
- World Health Organization. Updated recommendations on first-line and second-line antiretroviral regimens and post-exposure prophylaxis and recommendations on early infant diagnosis of HIV: interim guidelines. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. WHO/CDS/HIV/18.51. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-CDS-HIV-18.51.
-
- Nelson MR, Katlama C, Montaner JS, et al. The safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of HIV infection in adults: the first 4 years. Aids. 2007;21(10):1273–1281. - PubMed
-
- Sax PE, Zolopa A, Brar I, et al. Tenofovir alafenamide vs. tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in single tablet regimens for initial HIV-1 therapy: a randomized phase 2 study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2014;67(1):52–58. - PubMed
-
- Hall AM, Hendry BM, Nitsch D, Connolly JO. Tenofovir-associated kidney toxicity in HIV-infected patients: a review of the evidence. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011;57(5):773–780. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UM1 AI069423/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069456/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068632/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069530/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069399/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068616/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069436/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN275201800001I/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI131928/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN275201800001C/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI106716/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069436/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials