Assessment of liver graft quality during hypothermic oxygenated perfusion: The first international validation study
- PMID: 39251091
- PMCID: PMC11830552
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.08.030
Assessment of liver graft quality during hypothermic oxygenated perfusion: The first international validation study
Abstract
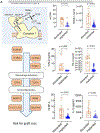
Background & aims: While it is currently assumed that liver assessment is only possible during normothermic machine perfusion, there is uncertainty regarding a reliable and quick prediction of graft injury during ex situ hypothermic oxygenated perfusion (HOPE). We therefore intended to test, in an international liver transplant cohort, recently described mitochondrial injury biomarkers measured during HOPE before liver transplantation.
Methods: Perfusate samples of human livers from ten centers in seven countries with HOPE experience were analyzed for released mitochondrial compounds, i.e. flavin mononucleotide (FMN), NADH, purine derivatives and inflammatory markers. Livers deemed unsuitable for transplantation served as negative controls.
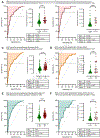
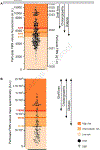
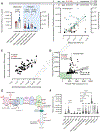
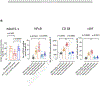
Results: We collected 473 perfusate samples of human donation after cardiac death (n = 315) and donation after brain death (n = 158) livers. Fluorometric assessment of FMN in perfusate was validated by mass spectrometry (R = 0.7011, p <0.0001). Graft loss due to primary non-function or cholangiopathy was predicted by perfusate FMN values (c-statistic mass spectrometry 0.8418, 95% CI 0.7466-0.9370, p <0.0001; c-statistic fluorometry 0.7733, 95% CI 0.7006-0.8461, p <0.0001). Perfusate FMN values were also significantly correlated with symptomatic non-anastomotic strictures and kidney failure, and superior for the prediction of graft loss than conventional scores derived from donor and recipient parameters, such as the donor risk index and the balance of risk score. Mitochondrial FMN values in liver tissues of non-utilized livers were low, and inversely correlated to high perfusate FMN values and purine metabolite release.
Conclusions: This first international study validates the predictive value of the mitochondrial cofactor FMN, released from complex I during HOPE, and may therefore contribute to a better risk stratification of injured livers before implantation.
Impact and implications: Analysis of 473 perfusates, collected from ten international centers during HOPE (hypothermic oxygenated perfusion), revealed that mitochondria-derived flavin mononucleotide values in perfusate are predictive of graft loss, cholangiopathy, and kidney failure after liver transplantation. This result is of high clinical relevance, as recognition of graft quality is urgently needed to improve the safe utilization of marginal livers. Ex situ machine perfusion approaches, such as HOPE, are therefore likely to increase the number of useable liver grafts.
Keywords: hypothermic machine perfusion; liver transplantation; liver utilization; mitochondria; outcome; viability assessment.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest JVG: has had funding from and is a consultant with Organ Recovery Systems, Itasca, IL. The other authors declare no conflict of interest. Please refer to the accompanying ICMJE disclosure forms for further details.
Figures



References
-
- Eden J, Sousa Da Silva R, Cortes-Cerisuelo M, et al. Utilization of livers donated after circulatory death for transplantation - An international comparison. J Hepatol, 2023. 78(5): p. 1007–1016. - PubMed
-
- de Meijer VE, Fujiyoshi M, Porte RJ. Ex situ machine perfusion strategies in liver transplantation. J Hepatol, 2019. 70(1): p. 203–205. - PubMed
-
- van Rijn R, Schurink IJ, de Vries Y, et al. Hypothermic Machine Perfusion in Liver Transplantation - A Randomized Trial. N Engl J Med, 2021. 384(15): p. 1391–1401. - PubMed
-
- Ceresa CDL, Nasralla D, Pollok JM, et al. Machine perfusion of the liver: applications in transplantation and beyond. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022. 19(3): p. 199–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

